Figure 2.
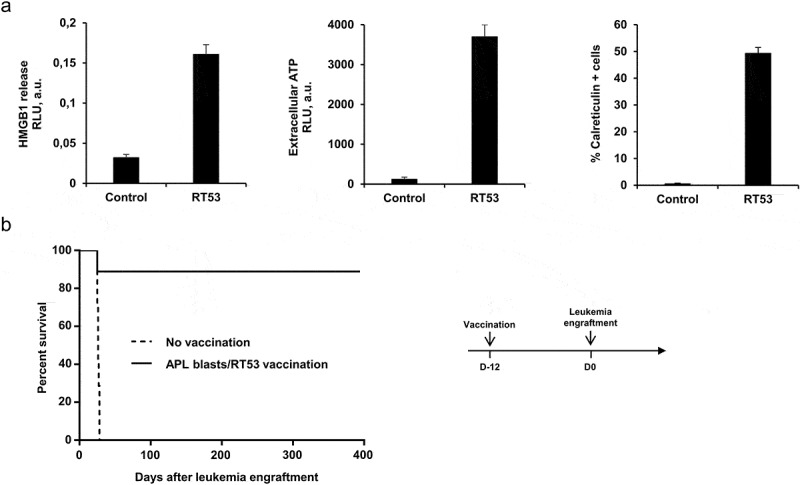
Inhibition of APL progression by prophylactic vaccination with RT53-treated APL blasts. (a) APL blasts in basal RPMI medium were left untreated or treated with either 5 μM of RT53 for 6 h (CRT exposure analysis) or 10 µM of RT53 for 1 h (HMGB1 and ATP release analysis). Extracellular HMGB1 (left) and ATP (middle) were then measured in the culture supernatant by ELISA and ATP-bioluminescence assays, respectively, and surface exposure of CRT (right) detected by FACS analysis. (b) APL blasts were exposed to 30 µM RT53 in basal RPMI medium for 3 h for cell death induction and the whole suspension was injected subcutaneously (2 × 106 cells) into the left flanks of FVB/N mice. Twelve days later, the vaccinated (n = 8) or control mice (n = 7) were injected i.v. with live 104 APL blasts. Survival curves were analyzed with the Mantel–Cox test. The schematic protocol used is illustrated (right).
