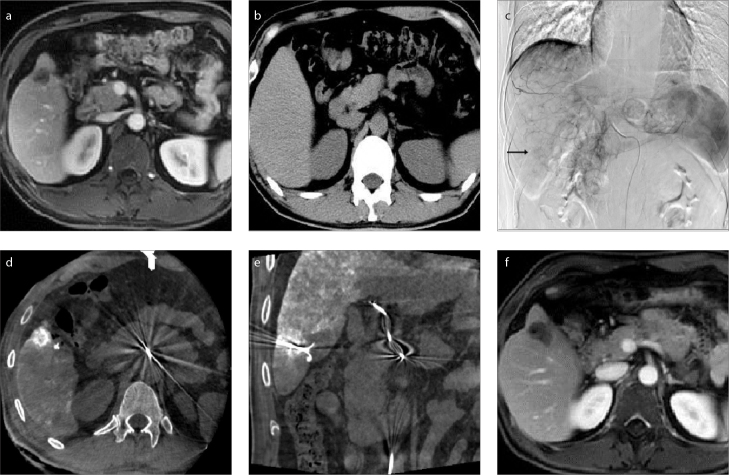
Figure 4. a–f.
Magnetic resonance image (a) shows a lesion behind the ribs. The lesion was invisible on US and conventional CT (b). TACE (c) was performed to mark the lesion (arrow) and embolize the lesion artery to reduce the risk of hemorrhage. Cone beam CT image (d) shows the lesion behind the ribs. In image (e), puncture was performed with a needle whose direction and position was adjusted, and ablation was started after confirmation of the needle position within the lesion by cone beam CT. Magnetic resonance image (f) shows complete necrosis achieved after ablation.