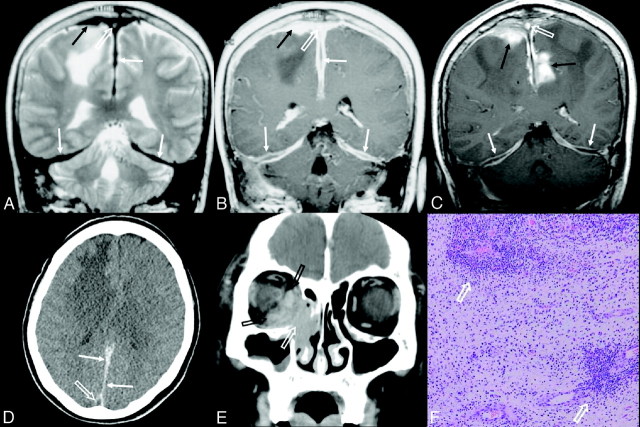
Fig 2.
Patient 6. A diffuse intracranial meningeal inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor in a 60-year-old woman showing multiple recurrences. A and B, At initial meningeal manifestation, coronal T2- (A) and postcontrast T1-weighted (B) images show diffuse dural thickening (white arrows) of T2 low SI with a nonenhancing central linear area in the enhancing thickened falx cerebri and bilateral tentorium, a homogeneously enhancing en plaque dural-based mass (black arrows) with extensive edema at the right frontal lobe, and dural venous sinus thrombosis with heterogenous T2 high SI and homogeneous enhancement at the superior sagittal sinus (white open arrows). C, Two years later, coronal postcontrast T1-weighted image shows an increase of the dural-based mass at the right frontal parasagittal convexity and a new development of the enhancing spiculated mass at the left parietal parasagittal area (black arrows), with persistent dural venous sinus thrombosis at the superior sagittal sinus (white open arrow). The enhancing thickened falx and tentorium show a decreased enhancement of the peripheral margin and an increased nonenhancing central linear area (white arrows). D, Transverse precontrast CT image shows diffuse thickening of posterior falx cerebri (white arrows) with high attenuation. The superior sagittal sinus (white open arrow) shows low attenuation and appears as a pseudoempty delta from the surrounding dural thickening. E, Four years after the initial meningeal manifestation, coronal orbit CT scan shows a homogeneously enhancing mass at the right nasolacrimal duct and adjacent right inferomedial orbital area (white open arrow) with destruction of the lamina papyracea. The inferior and medial rectus muscles are enlarged (black open arrows). F, Photomicrograph obtained at the right frontal dural-based mass from B shows multifocal areas of the predominant lymphoplasma cell infiltrations (white open arrows) in fibrovascular stroma mixed with myofibroblastic proliferation and a minor population of mixed inflammatory cells (HE, original magnification ×100).