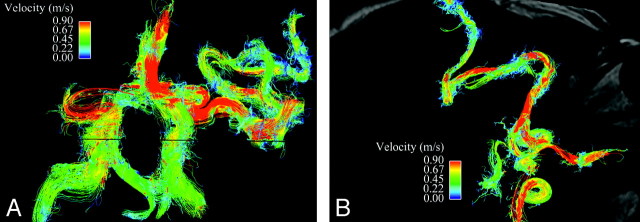
Fig 6.
Arterial inflow to the AVM. A is a streamline representation of the anterior and posterior intracranial circulation in an anteroposterior projection, with interrogation of the left middle cerebral artery branches leading to the AVM nidus. B overlays the same velocity data on an axial magnitude section at the level of the internal carotid arteries. Despite the marked tortuosity of these vessels and resulting disorganized flow, which limits streamline evaluation, regions of locally increased velocity within arterial feeders are easily identified and may help to predict the development of flow-related extranidal arterial aneurysms.