Fig 2.
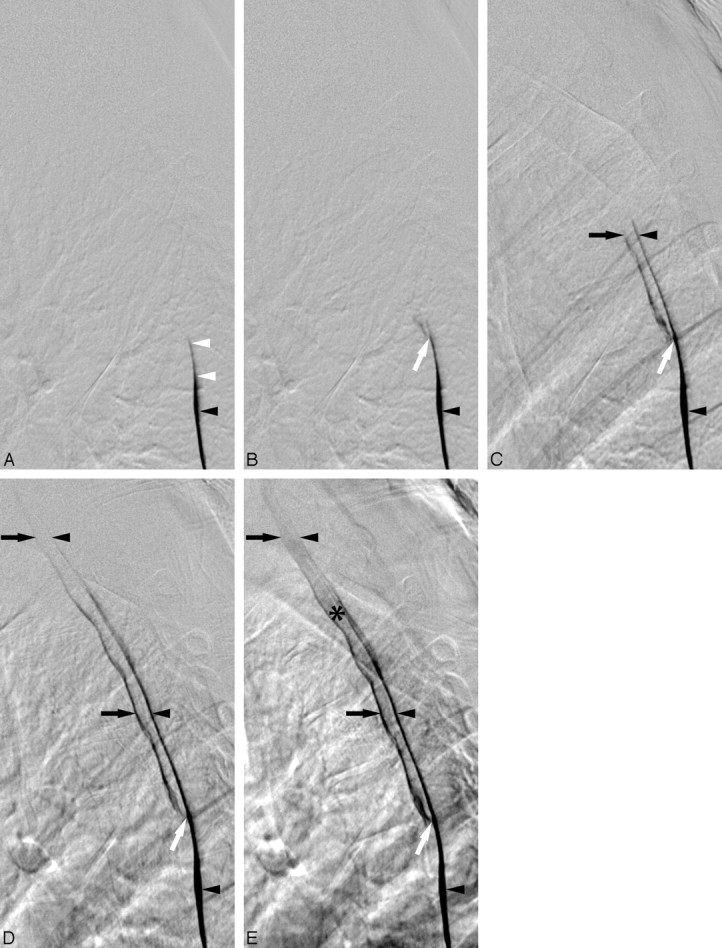
Lateral views of the thoracic spine acquired during digital subtraction myelography with the patient in the prone position. For temporal reference, the initial image is designated as time of (A) 0.0 second, and the subsequent images are at (B) 0.4 second, (C) 1.4 seconds, (D) 3.6 seconds, and (E) 11.2 seconds. Contrast is seen to progressively extend cephalad dependently within the thecal sac (black arrowheads). At T6–T7, the contrast slightly deviates dorsally because of mass effect on the dura by the caudal aspect of the epidural fluid collection (white arrowheads). Contrast focally extravasates through the ventral dural tear at T5–T6 (white arrow) into the epidural collection (black arrows). Contrast extends cephalad within both the thecal sac and the epidural collection. Ultimately, the epidural fluid collection becomes more dense (*) because of its smaller volume relative to the subarachnoid space.
