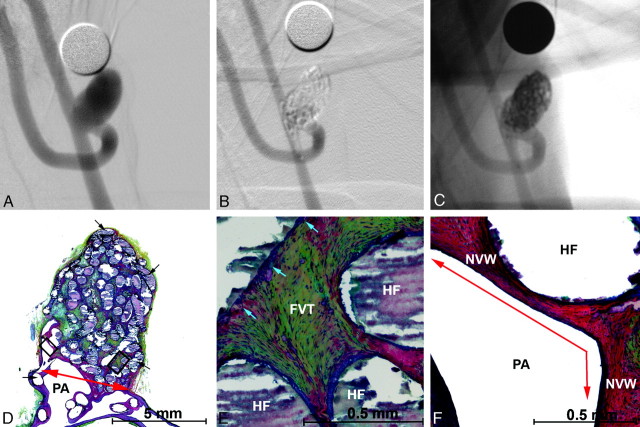
Fig 4.
Angiographic and histologic images of aneurysm treated with PEG-B devices with a 3F microcatheter. A, Preembolization DSA, 6.0 × 9.3 mm (dome x length). B, Posttreatment DSA showing dog ear filling with parent artery compromise. C, Posttreatment, nonsubtracted angiographic image showing the radiopacity of the hydrogel filaments. D–F, Methyl methacrylate embedded, Movat pentachrome–stained microtome sections of the aneurysm. D, Aneurysm overview showing hydrogel filaments (black arrows), neointima covered neck (red arrow), and the parent artery (PA). E, Enlarged right-hand square from D. Fibrovascular tissue (FVT) between hydrogel filaments (HF) and mild inflammation (blue arrows). F, Enlarged left-hand square from D. Hydrogel filaments (HF) supporting a thick new vessel wall that traverses the aneurysm neck (red arrow).