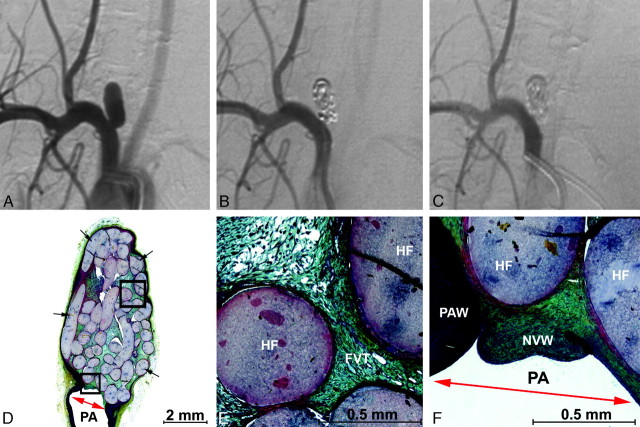
Fig 5.
Angiographic and histologic images of aneurysm treated with PPG-B devices with a 3F microcatheter. A, Preembolization DSA, 3.0 × 8.0 mm (dome × length). B, Posttreatment DSA showing complete occlusion without parent artery compromise. C, A 6-week follow-up DSA showing complete occlusion without parent artery compromise. D–F, Methyl methacrylate embedded, Movat pentachrome–stained microtome sections of the aneurysm. D, Aneurysm overview showing densely packed hydrogel filaments (black arrows) and a new vessel wall covering the neck (red arrow). E, Enlarged upper square from D. Fibrovascular tissue (FVT) between hydrogel filaments (HF) and mild inflammation. F, Enlarged lower square from D. Hydrogel filaments (HF) supporting a thick new vessel wall that traverses the aneurysm neck (red arrow) and adheres to the parent artery wall (PAW).