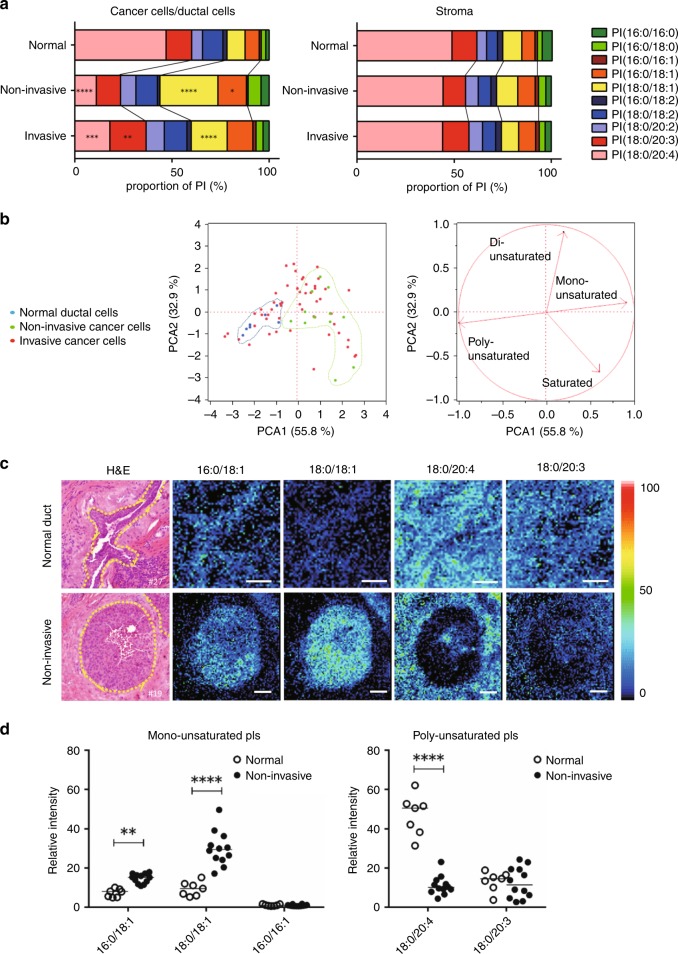
Fig. 2.
Replacement of PI(18:0/20:4) with PIs-MUFA as a common process of in situ breast cancer growth. a Left: the averaged FA composition of PIs detected in cancer cells and adjacent normal ductal cells. Right: the averaged FA composition of PIs detected in the surrounding stromal areas. * indicates a statistically significant difference in the comparison between normal ductal cells and non-invasive cancer cells or between non-invasive cancer cells and invasive cancer cells. Saturated, monounsaturated, di-unsaturated and polyunsaturated PIs are coloured in blue, yellow, red and green, respectively. Two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s post hoc multiple comparisons test. **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. b Principal component analysis of normal ductal cells and cancer cells based on the proportion of ten PIs. Left: each dot indicates an individual lesion. Blue: normal ductal cells; green: non-invasive cancer cells; red: invasive cancer cells. Right: the arrows indicate the contribution rate of PIs with different degrees of unsaturation. The contribution ratio of each component is displayed on the axis. c Representative histological mapping of PIs and the corresponding H&E staining. Upper panels: images of normal ductal cells and their associated stroma. Lower panels: images of non-invasive cancer cells and stroma. Normal ductal cells and cancer cells are encircled by a yellow dotted line in H&E staining. Relative intensity of ion signals is represented by an RGB scale. Scale bar (white): 50 μm. d Comparison of relative intensities between non-invasive cancer cells and normal ductal cells. White and black circles show individual lesions of normal ductal and non-invasive cancer cells, respectively. * indicates a statistically significant difference in the comparison between normal and non-invasive cancer cells. Two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s post hoc multiple comparisons test. **p < 0.01; ****p < 0.0001.