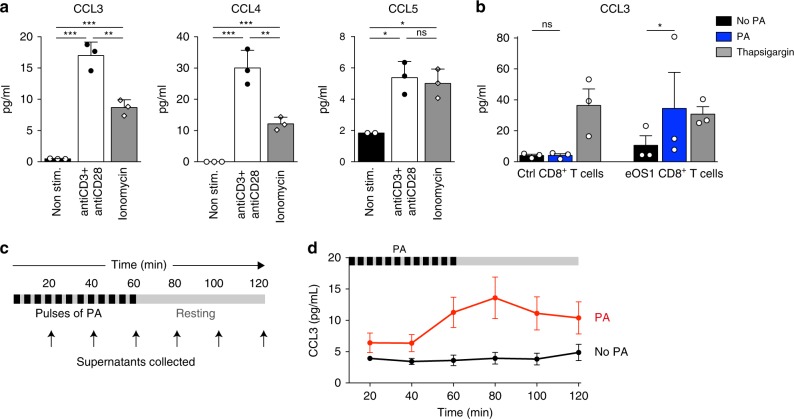
Fig. 3. The eOS1 actuator allows to control the rapid chemokine release in T cells.
a Effector primary CD8+ T cells were stimulated for 1 h at 37 °C with anti-CD3 + anti-CD28-coated antibodies or with ionomycin or were left unstimulated. Supernatants were recovered and the secretion of the chemokines CCL3, CCL4, and CCL5 were measured using a mouse cytokine multiplex assay. Representative of two independent experiments. Results are shown as mean ± SEM. Dots correspond to experimental replicates. Statistical significance was assessed using a two-tailed unpaired t-test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). b Primary CD8+ T cells were transduced with eOS1 (or with eGFP as a control) and the calcium pathway was stimulated for 1 h either by photoactivation or thapsigargin. The secretion of CCL3 was measured in the supernatants by ELISA. Results are compiled from three independent experiments (each dot represents one experiment, histograms show mean ± SEM). Groups were compared using a ratio paired t-test. (*p < 0.05). c, d Kinetic of CCL3 secretion after photoactivation. Primary CD8+ T cells transduced with eOS1 were photoactivated with 5 s pulses of light every 5 min during 1 h and left non photoactivated for an additional hour. Supernatants were collected every 20 min and replaced by warm medium. c Experimental setup. d CCL3 secretion was measured by ELISA in the supernatants of photoactivated cells (red curve) or control non photoactivated cells (black curve). The results of three independent experiments are pooled and shown as mean ± SEM. Source data are provided as a Source Data File.