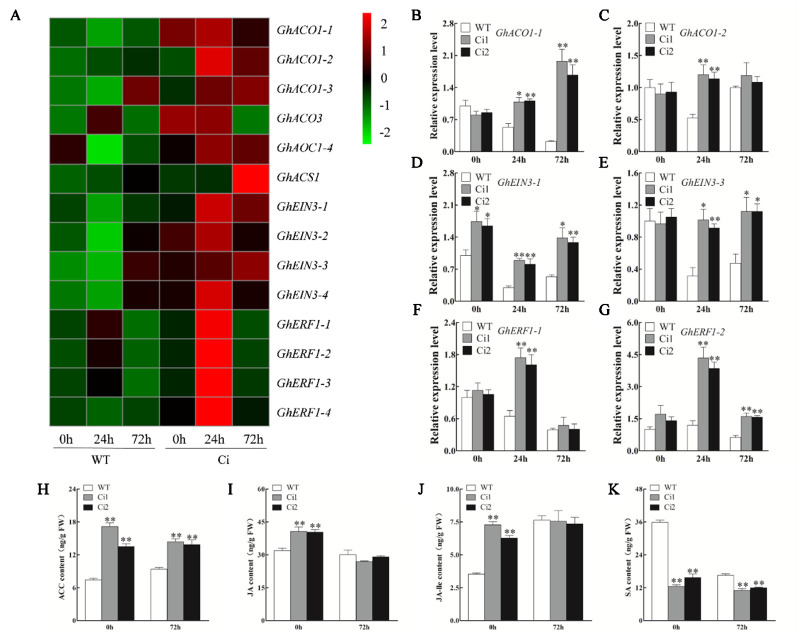
Figure 6.
Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR analysis of the expression level of the ethylene (ET) biosynthesis and response genes, and the content of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic (ACC), jasmonic acid (JA), JA-isoleucine (JA-Ile), and salicylic acid (SA) in the WT and GhWRKY70D13-RNA interference (RNAi) plants inoculated with Verticillium dahliae. (A) Comparison of the expression patterns of the ET biosynthesis and response genes in the WT and Ci plants infected by V. dahliae based on RNA-seq. (B–G) Relative expression levels of (B) GhACO1-1, (C) GhACO1-2, (D) GhEIN3-1, (E) GhEIN3-3, (F) GhERF1-1, (G) GhERF1-2 at 0, 24, and 72 h after inoculation with V. dahliae in the WT, Ci1, and Ci2 plants. (H–K) The content of (H) ACC, (I) JA, (J) JA-Ile, and (K) SA in the WT, Ci1 and Ci2 plants at 0 h and 72 h after inoculation with V. dahliae. WT, wild-type; Ci1 and Ci2, two independent GhWRKY70D13-RNAi cotton lines; Ci, a mixed sample of GhWRKY70D13-RNAi line 1 (Ci1) and GhWRKY70D13-RNAi line 2 (Ci2). Each experiment was performed using three independent biological replicates. Differences between wild-type and transgenic plants were compared using the Student's t-test (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01).