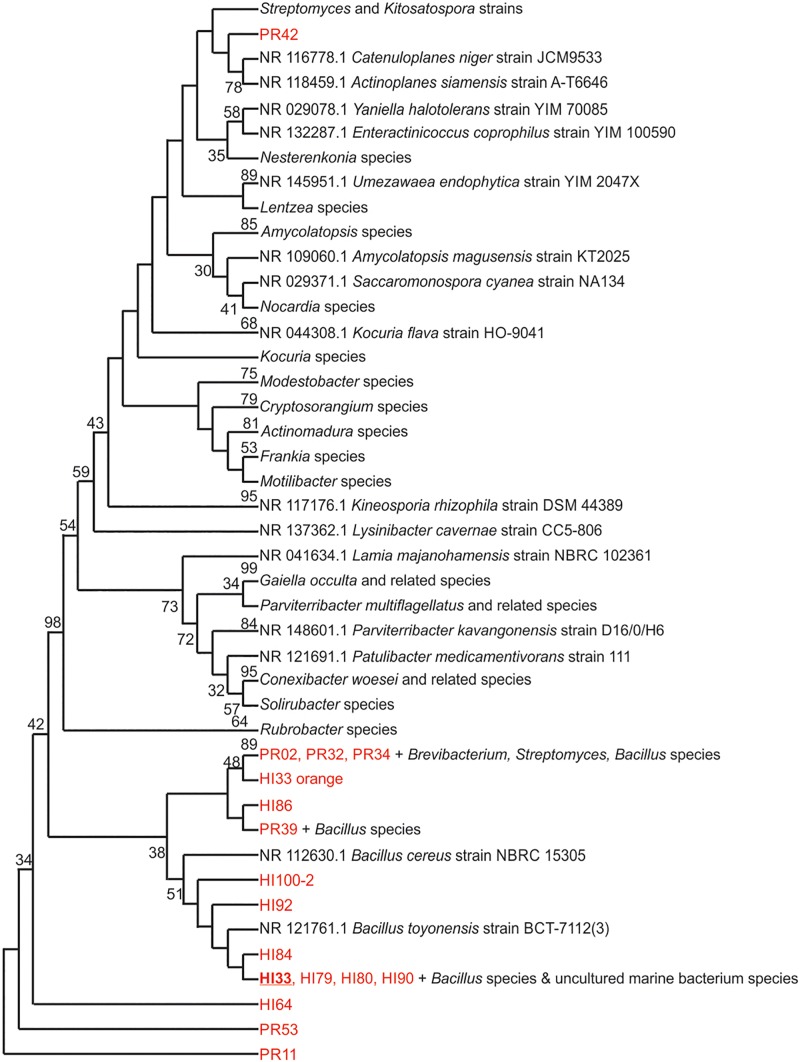
FIGURE 3.
Evolutionary relationships of bacterial strains were analyzed. The evolutionary history was inferred using the Neighbor-Joining method (Saitou and Nei, 1987). The bootstrap consensus tree inferred from 500 replicates (Felsenstein, 1985) is taken to represent the evolutionary history of the taxa analyzed. Branches corresponding to partitions reproduced in less than 50% bootstrap replicates are collapsed. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (500 replicates) are shown next to the branches (Felsenstein, 1985). The evolutionary distances were computed using the Maximum Composite Likelihood method (Tamura et al., 2004) and are in the units of the number of base substitutions per site. The analysis involved 125 nucleotide sequences. All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated. There were a total of 153 positions in the final dataset. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA7 (Kumar et al., 2016).