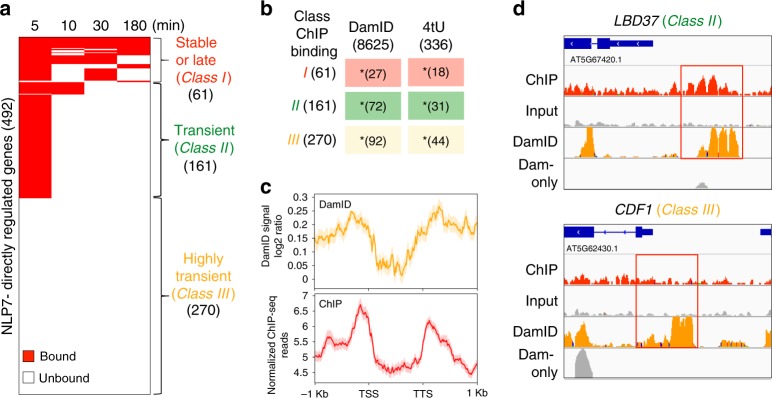
Fig. 2. Transient and highly transiently bound NLP7 actively transcribed targets are captured by time-series ChIP and/or DamID.
a Intersection of NLP7 directly regulated genes and NLP7-bound genes captured by time-series ChIP-seq (minutes after DEX-induced nuclear import). Red bars indicate genes that are bound and directly regulated by NLP7. Intersection of these datasets revealed three distinct classes of direct NLP7-regulated targets: (Class I) stable or late, (Class II) transient, (Class III) highly transient. b DamID captures a significant proportion of genes belonging to all three classes, including NLP7–target interactions that were missed by ChIP (Class III). Genes from all three classes are enriched in genes whose active transcription is induced by NLP7 (4tU-labeled). Fisher’s exact test *p-value < 0.001. c The profile of DamID, indicated by the number of normalized DamID sequencing reads in the 1000-bp upstream regions of TSS to the 1000-bp downstream regions of TTS. The DamID profile is similar to the ChIP profile, indicated by the normalized ChIP-seq reads. d LBD37 is an example of active NLP7-initiated transcription (4tU) where binding is captured by both DamID (orange) and ChIP (red). CDF1 is an example of active NLP7-initiated transcription in which TF binding is captured by DamID, but missed by ChIP.