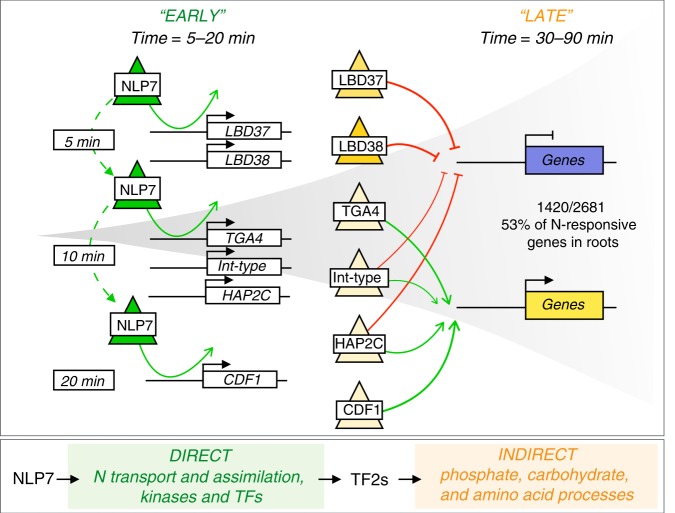
Fig. 6. A validated model for NLP7 role in rapidly initiating a cascade that amplifies the downstream N-response.
Transient interactions of NLP7 initiate early N-response genes including genes involved in N-uptake and early N-response TFs. The transient interactions of NLP7 enable it to rapidly activate secondary TFs leading to a transcriptional burst in a short period of time. Secondary TFs amplify the NLP7-initiated cascade by regulating downstream late N response genes enriched in phosphate, carbohydrate, and amino acid processes (Supplementary Data 26). LBD37 and LBD38 primarily mediate transcriptional repression, and both have been shown to have in planta relevance18; CDF1 and TGA4 primarily mediate transcriptional activation; and Int-type and HAP2C act as either gene activators or repressors depending on the target downstream of NLP7. Collectively, the direct targets of NLP7 and direct targets of secondary TFs account for 53% of the N response in plant roots19.