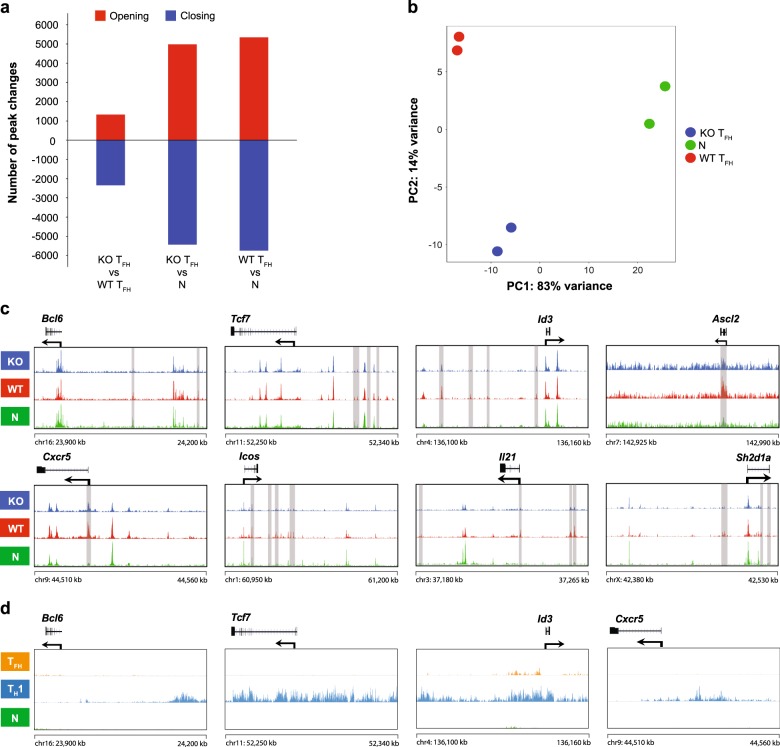
Fig. 6.
Role of EZH2 in the remodeling of TFH lineage-associated chromatin accessibility during viral infection. a Numbers of chromatin peaks with differential accessibility (FDR < 0.05; FC > 1.5) in naïve CD4+ T cells (N), WT TFH cells and KO TFH cells. b PCA plot of the peak accessibilities in naïve CD4+ T cells (green), WT TFH cells (red) and KO TFH cells (blue). Each dot represents a replicate of the group. c ATAC-Seq signal profiles of TFH lineage-associated gene loci in naïve CD4+ T cells (N), WT TFH cells and KO TFH cells. d Tracks of H3K27me3 ChIP-Seq data from TFH lineage-associated gene loci in naïve CD4+ T cells (N), TFH cells and TH1 cells. The data were obtained from two independent experiments with one biological replicate (pooled from at least five mice per group) in each experiment (a–c) and from one experiment with one biological replicate (d)