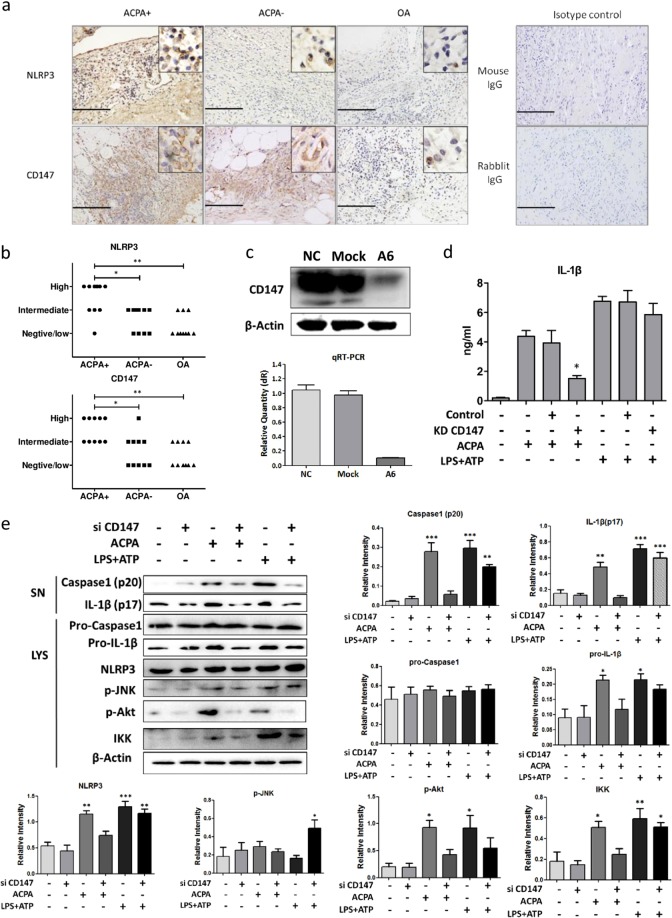
Fig. 2.
CD147 participates in anti-citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA)-induced NLRP3 upregulation and activation. a Representative tissue sections from ACPA+ rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, ACPA− RA patients, and osteoarthritis patients analyzed by immunohistochemical (IHC) methods to determine the expression of NLRP3 and CD147. Images of IHC staining with irrelevant rabbit or mouse immunoglobulin G as the isotype control are also shown. Scale bar = 100 μm. b Statistical results of interleukin (IL)-1β staining. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01. c The real-time PCR and western blotting results indicated successful knockdown of CD147 mRNA and protein expression (by approximately 90% of the original expression levels) by lentiviral transduction. d After CD147 knockdown, peripheral blood mononuclear cell-derived macrophages were stimulated with ACPAs or lipopolysaccharide/ATP. Cells infected with empty virus served as the control. IL-1β production in the culture medium was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. e Representative results and statistical analysis of caspase1 (p20), IL-1β (p17), pro-caspase1, pro-IL-1β, NLRP3, p-JNK, p-Akt, and IKK protein expression as determined by western blotting after the indicated treatments. Each experiment was performed at least three times. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 (other groups vs. the first group). SN supernatant, LYS cell lysate