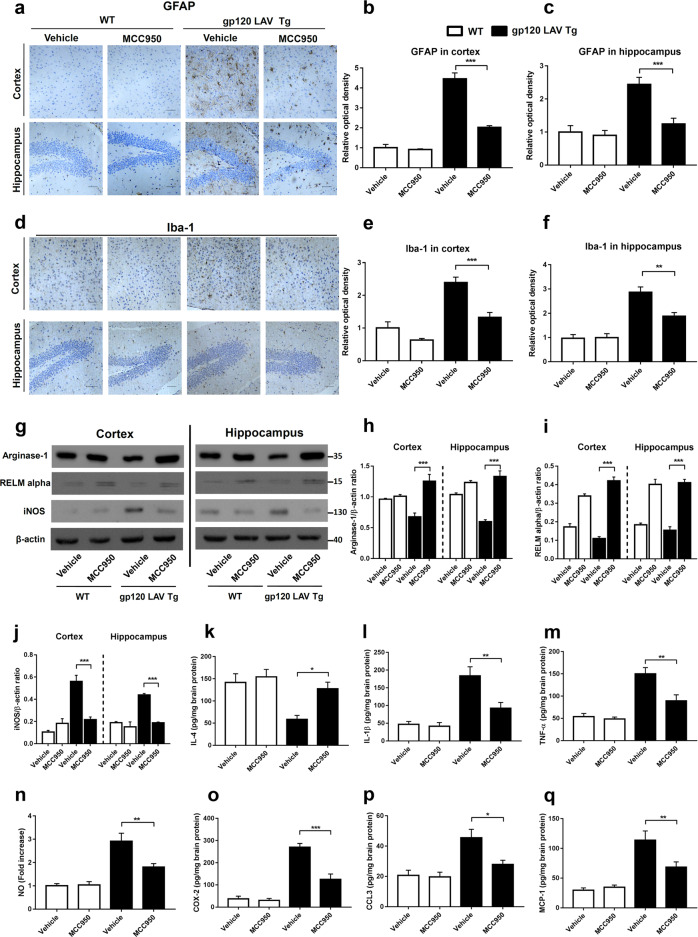
Fig. 7.
Effect of MCC950 on neuroinflammation and microglia polarization in gp120 LAV Tg mice. Brain sections of WT (n = 3) and gp120 LAV Tg (n = 3) mice chronically administered vehicle (PBS, 80 days) or MCC950 (10 mg/kg BW, dissolved in PBS, 80 days) were assessed for the degree of neuroinflammation. Serial brain sections of the cortex (upper panels) and hippocampus (lower panels) were immunostained with GFAP (a) and Iba-1 (d) and analyzed quantitatively using ImageJ software (b, c, e, f). Scale bar: 100 μm. g–j Western blots (g) and densitometric analysis of arginase-1 (h), RELM alpha (i), and iNOS (j) in the cortex and hippocampus of WT (n = 5) and gp120 LAV Tg mice (n = 5) administered vehicle or MCC950. k–q Production of IL-4 (k), IL-1β (l), TNF-α (m), NO (n), COX-2 (o), CCL3 (p), and MCP-1 (q) in brain tissue homogenates of WT (n = 6) and gp120 LAV Tg (n = 6) mice treated with vehicle or MCC950. Data are displayed as the mean ± SEM (n = 5, h–j) and (n = 6, b, c, e, f, k–q) are from two independent experiments. The immunohistochemical staining and Western blot results are representative of two independent experiments (a, d, g). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001