Fig. 1.
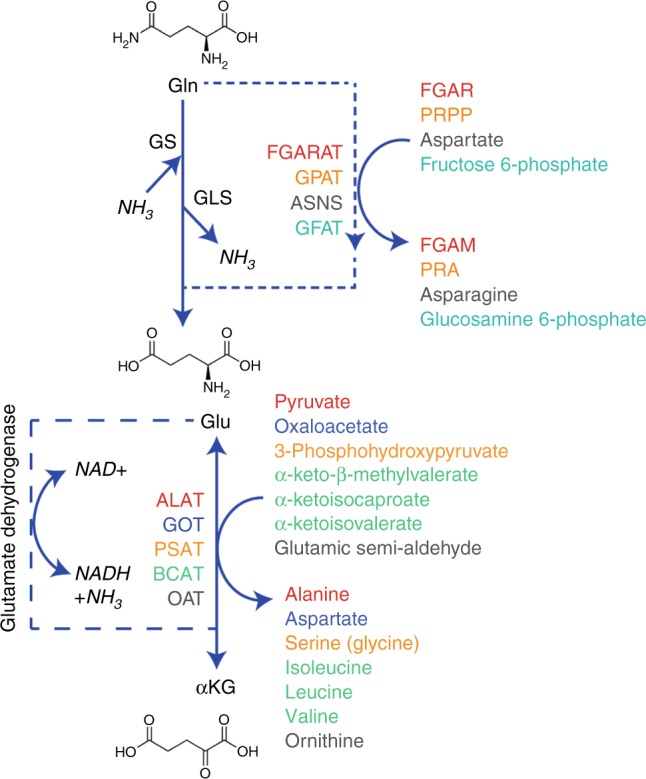
Metabolism of glutamine. The amido group of glutamine is involved in relatively few reactions in addition to deamidation, some major examples are indicated. Transamination, for which only some representative reactions are shown, involves a number of 2-oxoacids that can be reversibly converted into the amino acid. Colours are used in both sets of reactions to indicate the enzyme (left) responsible for the reaction (right). On the left are the reactions that require, or evolve ammonia as part of the metabolism of glutamine to or from α-ketoglutarate. Abbreviations: αKG α-ketoglutarate, ALAT, alanine aminotransferase, ASNS, asparagine synthetase, BCAT, branched-chain aminotransferase, FGAM 5′-phosphoribosyl-N-formylglycinamidine, FGAR 5′-phosphoribosyl-N-formylglycinamide, FGARAT FGAR amidotransferase, GFAT glutamine fructose 6-phosphate amidotransferase, Gln glutamine, GLS glutaminase, Glu glutamate, GPAT glutamine phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate amidotransferase, GOT glutamic-oxaloacetic aminotransferase, GS glutamine synthetase, OAT ornithine aminotransferase, PRA 5′-phosphoribosyl-1-amine, PRPP 5′-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate, PSAT phosphoserine aminotransferase.
