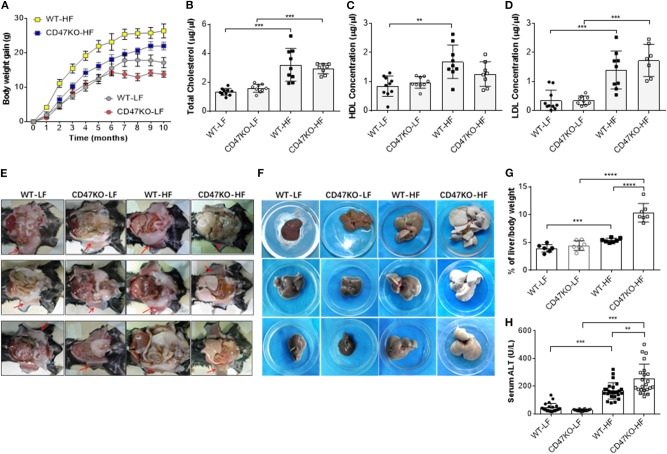
Figure 1.
A high-fat diet (HFD) induces more severe liver injury in CD47KO mice. (A) Net body weight gains (n = 7 mice/group). A representative of two independent experiments is shown. (B–D) Serum levels of total cholesterol (B), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL) (C), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL) (D) measured at the end of the experiments (n = 7–10). Shown are results from a representative of two independent experiments. (E,F) Autopsy showing subcutaneous fat (E, arrowhead) and hepatomegaly (F). (G) Ratios (%) of liver to body weight (n = 7 mice/group). (H) Serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels (n = 22–25; combined from four independent experiments). Data are presented as mean ± SD. **p < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; and ****P < 0.0001.