Fig. 2.
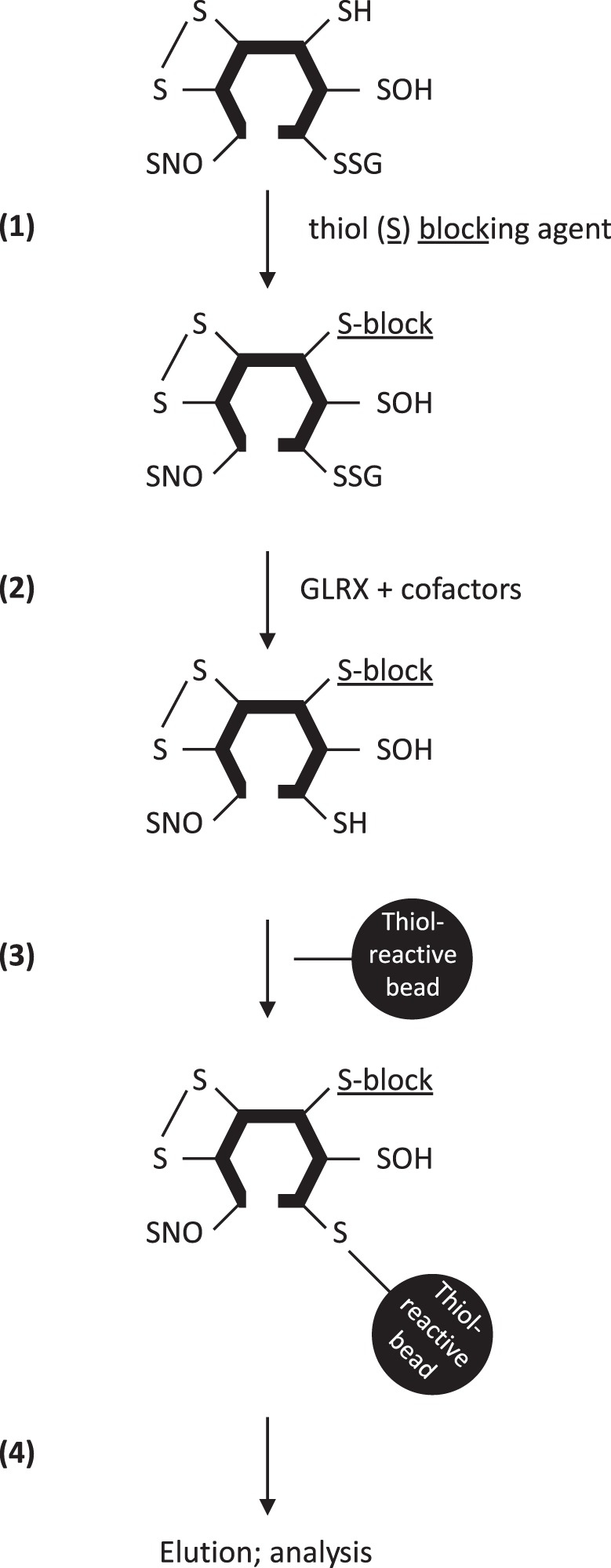
Schema summarizing the steps required to identify S-glutathionylated proteins using glutaredoxin-1 (GLRX)-based derivatization and thiol affinity capture. Existing free thiols in proteins are first blocked by thiol-blocking agents (1). S-glutathionylated cysteines are thereafter derivatized by adding GLRX and cofactors (2), resulting in the emergence of new free thiols. New thiols are enriched using thiol-reactive beads (3), and enriched proteins are eluted thereafter for further analysis (4), using mass spectrometry or Western blotting as examples. We refer the reader to the text for detailed descriptions about these procedures.
