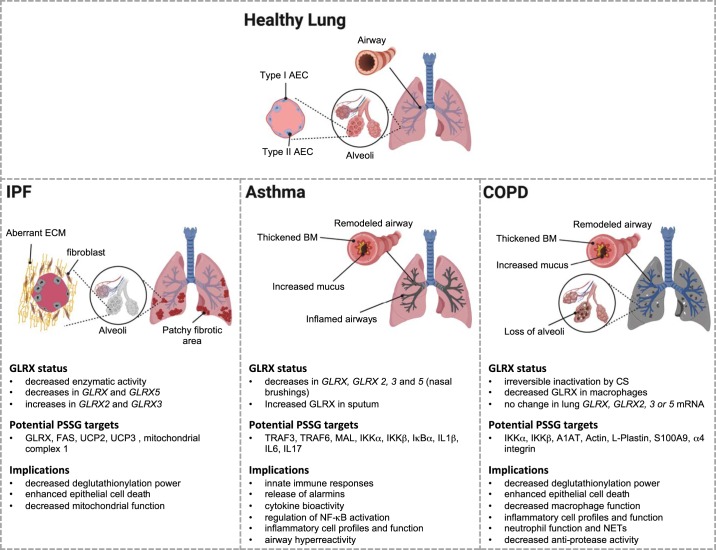
Fig. 5.
Summary of how an altered glutaredoxin-1/protein S-glutathionylation (GLRX/PSSG) status affects idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), asthma, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The main pathophysiological features that accompany these diseases are represented graphically. The text below summarizes what is currently known about GLRX status in these diseases. Potential PSSG targets are also indicated. Please note that many of these were derived from rodent models or cell-based studies with disease-relevant stimuli, but the majority will need to be validated in human specimens. As is described in the text, S-glutathionylated proteomes in human tissues also remain to be unraveled. Nonetheless, the proteins that were found to be S-glutathionylated are believed to have substantial implications for a number of processes and pathways that are listed and are known to control the pathogenesis of these chronic respiratory diseases. [Created with BioRender.]