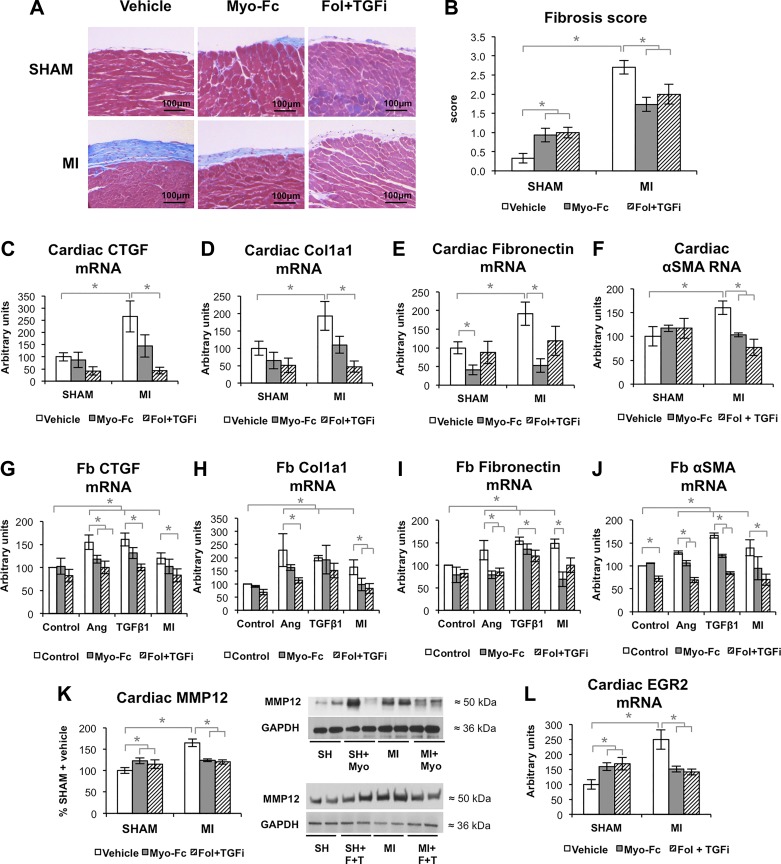
Fig. 6.
Inhibition of activin type II receptor (ACTRII)/TGFβ receptor (TGFBR) signaling prevents fibrosis after experimental myocardial infarction (MI). A and B: representative images of epicardial fibrosis (A) and fibrosis score (B) of sham and mice with MI treated with vehicle, Myo-Fc, or a combination of follistatin and a TGFβ receptor inhibitor (Fol + TGFi); n = 6 mice/group. C–F: cardiac mRNA levels of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF; C), type I collagen (Col1a1; D), fibronectin (E), and α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA; F); n = 5 mice/group. mRNA levels of CTGF (G), Col1a1 (H), fibronectin (I) and α-SMA (J) in cultures of human ventricular cardiac fibroblasts (Fb) treated for 24 h with sham (control) or 10 wk post-MI mouse serum (MI), angiotensin II (ANG II; 10 μM) or TGFβ1 (10 ng/ml) in the presence or absence of 0.2 μg/ml Myo-Fc or a combination of follistatin (10 ng/ml) and a TGFβ receptor inhibitor (1 μM; Fol + TGFi). K: cardiac protein levels of matrix metalloproteinase 12 (MMP12) and representative blots, n ≥ 8 mice/group. L: cardiac early growth response gene-2 (EGR2) mRNA; n = 5 mice/group. *P < 0.05 by 2-way ANOVA.