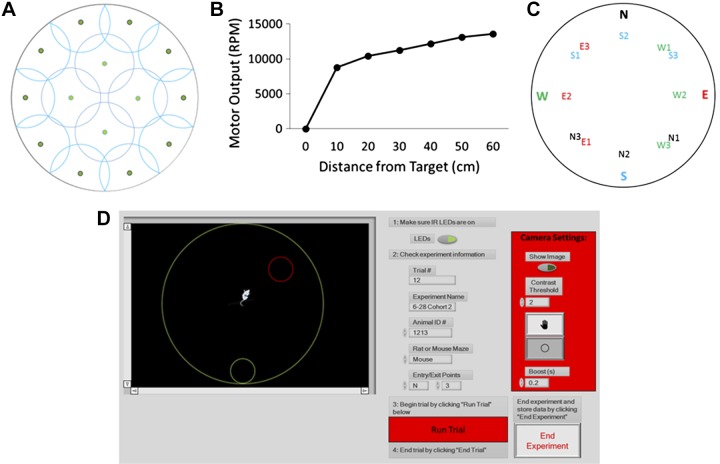
Fig. 2.
A circle packing algorithm was used to determine the optimal placements of motors (green dots) on the underside of the open field (A). Change in vibration motor output as a function of mouse distance from the target location (B). Maze exit points were randomized via a Latin square design between 12 possibilities (N1, N2, N3, E1, E2, etc.). Each exit point was equidistant from its corresponding entrance point (designated north, east, west, or south; C). The graphical user interface prompted experimenters to turn on LEDs and to input trial information (trial name, date, animal name, species, and entrance point) as well as start and end each trial. The experimental field boundaries, region of interest, and the contrast threshold settings were also controlled by the interface (D).