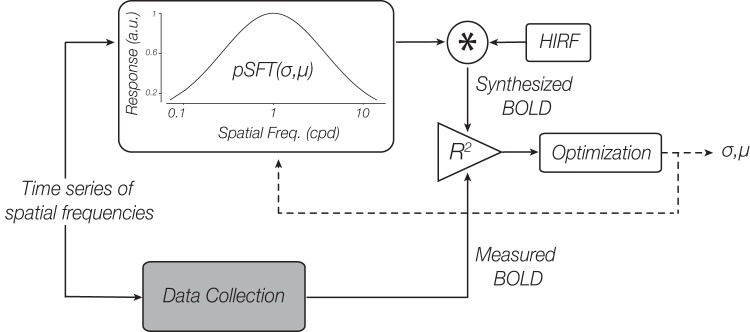
Fig. 2.
Schematic diagram of the proposed model-based approach. Blood oxygen level-dependent (BOLD) time series containing responses to varying spatial frequencies were both measured and synthesized. The synthesized BOLD response was calculated by convolving the hypothetical neural responses to the frequencies, i.e., the pSFT values at the tested frequencies with the hemodynamic impulse response function. The population spatial frequency tuning (pSFT) was modeled as a log Gaussian function (Eq. 1) with unknown mean (µ) and SD (σ). Through comparison of the measured BOLD response with the synthesized one, the unknown parameters of the pSFT were estimated. The R2 of the fit of the 2 time series is the index of similarity, and the final estimated parameters are the outputs of a recursive optimization procedure, with the goal of maximizing the similarity index; cpd, cycles/degree; a.u., arbitrary units; HIRF, hemodynamic impulse response function; *, convolution operation.