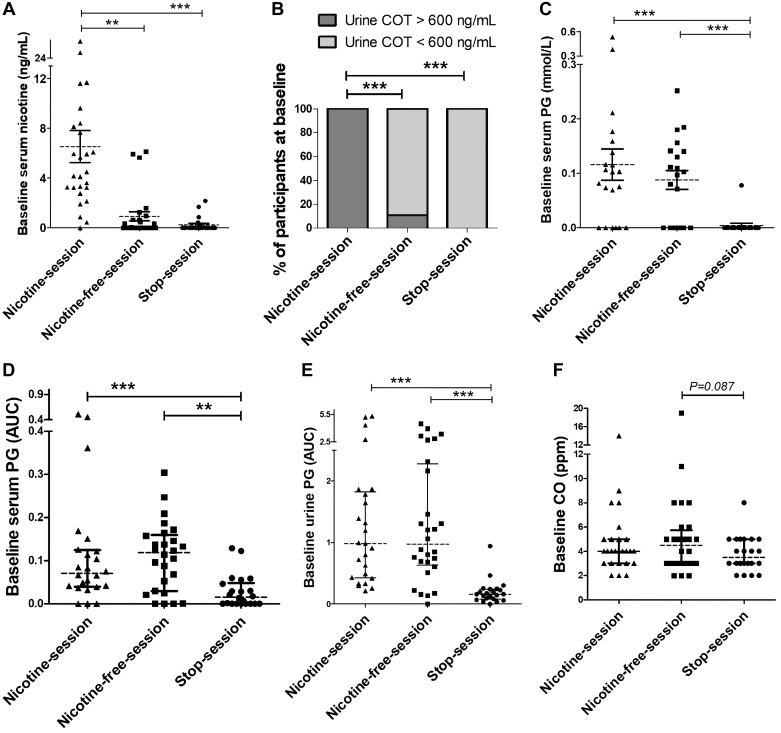
Fig. 2.
Baseline values of serum nicotine (A), semiquantitative assessment of urine cotinine (COT) (B), serum propylene glycol (PG) assessed by gas chromatography with a flame ionization detector (C), area under the curve (AUC) of serum PG assessed by 1H-NMR spectroscopy (D), AUC of urine PG (1H-NMR spectroscopy) (E), and exhaled carbon monoxide (CO) (F). Horizontal brackets represent the P values for the comparison between baseline values in each session. A mixed-effects linear model analysis was performed with experimental sessions and time points as fixed effects and baseline values as random effects (random intercept model). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Data represent the mean ± SE.