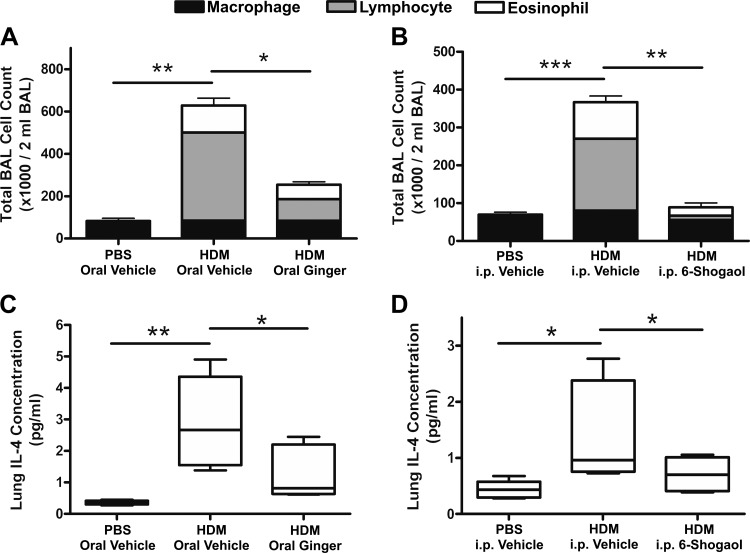
Fig. 2.
Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cell counts and lung IL-4 concentrations. Ten days of intranasal house dust mite (HDM) exposure led to a significant increase in total BAL cell counts in oral and intraperitoneal (ip) vehicle-treated control animals (A and B, respectively) compared with corresponding intranasal phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) vehicle controls. These increases, which were composed primarily by elevations in eosinophil and lymphocyte numbers, were significantly inhibited by coadministration of oral whole ginger extract (A; 40 mg/kg twice daily) or intraperitoneal 6-shogaol (B; 50 µL ip of 6.6 mM solution twice daily). Oral whole ginger extract and intraperitoneal 6-shogaol also significantly inhibited HDM-mediated increases in lung homogenate IL-4 concentration (C and D, respectively). Data in A and B are means ± SE, n = 5 mice, ANOVA with Bonferonni posttest comparisons. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.