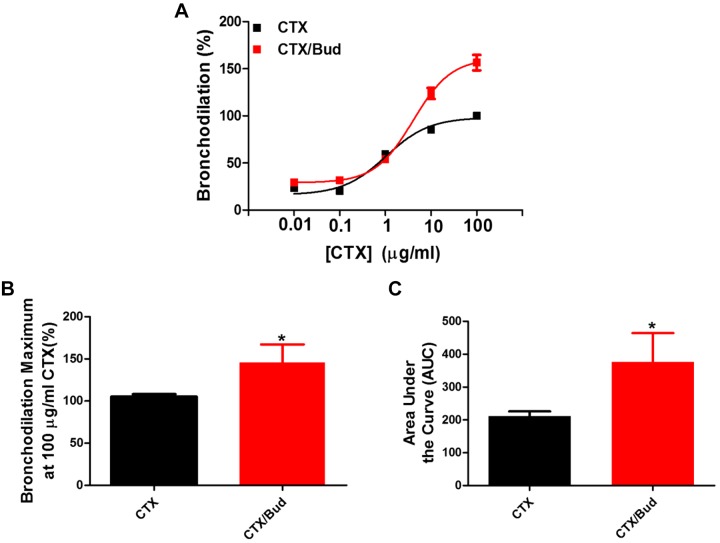
Fig. 3.
Budesonide significantly augments cholera toxin-induced bronchodilation of human small airways. Budesonide (10 μM) was given simultaneously with cholera toxin (CTX, 0.01–100 μg/mL) and bronchodilation was assessed. Concentration-response curves (A) were normalized to CTX stimulation alone set to 100%. Maximum bronchodilation at 100 μg/mL (B, CTX vs. CTX + budesonide at a maximum of 100 μg/mL CTX, 105.5 ± 3.9% vs. 128.4 ± 17.5%) and area under the curve (AUC) (C, CTX vs. CTX + budesonide, 200.8 ± 13.8 vs. 361.5 ± 112.6) were significantly increased with budesonide stimulation. Data are representative of n = 5 donors, 11–13 slices/condition. *P < 0.05 compared with CTX stimulation alone.