Fig. (1).
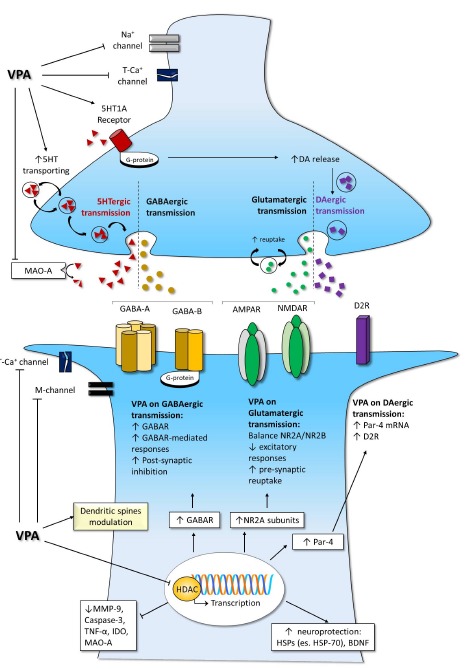
Valproate effects on synaptic cleft and intracellular pathways. The increase in GABAergic transmission pairs with a modulation other aminergic systems; the excitatory ionic channels, such as calcium and sodium channels, are negatively modulated, while potassium currents are enhanced. Moreover, epigenetic mechanisms influence receptor expression and neuroprotective pathways. Legend. AMPAR: α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid –AMPA- receptor; BDNF: brain derived neurotrophic factor; DA: dopamine; D2R: dopamine D2 receptor; GABA: gaba-amino-butirric acid; GABAR: GABA receptors; GABA-A: GABA receptor type A; GABA-B: GABA receptor type B; HSPs: heat shock proteins; HSP-70: heat shock protein 70; K+: potassium; IDO: indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase; MAO-A: mono-amines oxidase type A; M-channel: low-threshold noninactivating voltage-gated potassium current; MMP-9: metalloproteinases-9; Na+ channel: sodium channel; NMDAR: N-metyl-D-aspartate -NMDA- receptor; NR2A: 2A subunit of NMDAR; NR2B: 2B subunit of NMDAR; Par-4: prostate apoptosis response-4; T-Ca+ channel: low-threshold T-calcium channel; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor α; VPA: valproate; 5HT: serotonin.
