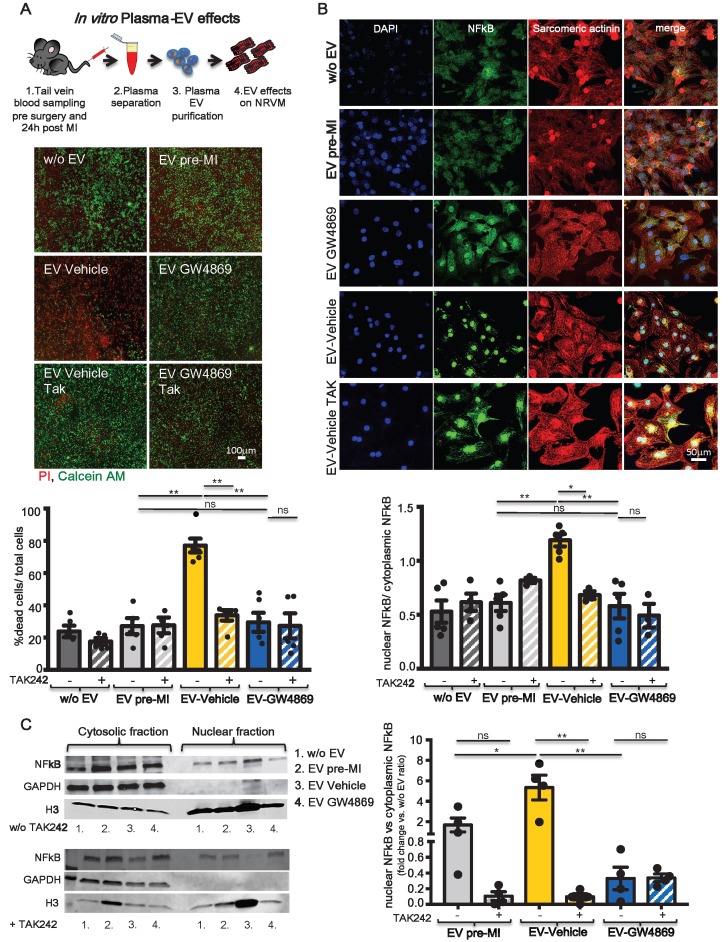
Figure 6.
TLR4-NFkB axis regulates in vitro plasma-derived EV effects. (A) Quantification of plasma derived EV cytotoxicity on rat primary neonatal cardiomyocytes (NRVM) using the TLR4-specific inhibitor TAK242. Representative images of 5 independent experiments treated with 5 different pools of EV. Viable cells stain green, dead cells red. (B) Evaluation of NFkB nuclear translocation in NRVM. DAPI mask was used to detect NFkB nuclear fraction. Dots in graphs represent the number of different plasma-derived EV tested in each experimental condition. (C) WB analysis and quantification of nuclear translocation of NFkB (n=4 independent experiments). Quantification data are presented as nuclear/cytosol ratio within the same treatment and expressed as mean fluorescent intensity fold change versus w/o EV. All data are presented as mean ± SEM and analyzed by one-way ANOVAs with post-hoc Bonferroni multiple comparisons correction (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). Mean, SEM and statistics are reported in full in Table S6.