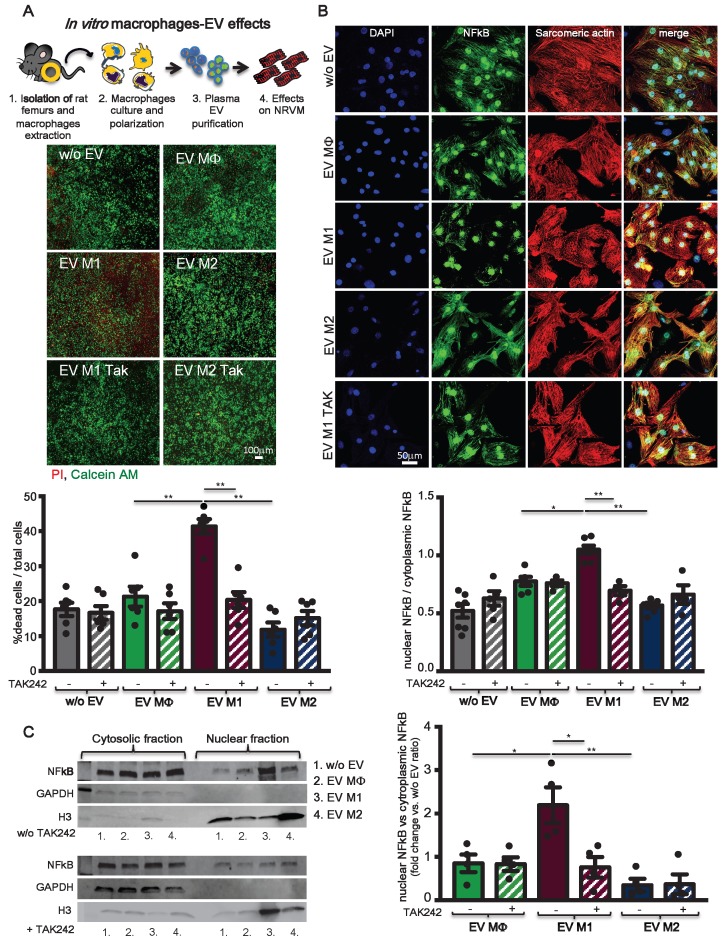
Figure 8.
TLR4-NFkB axis regulates in vitro macrophages-derived EV effects. (A) Evaluation of BMDM derived EV cytotoxicity on rat primary neonatal cardiomyocytes using the TLR4-specific inhibitor TAK242. Data refers to 6 independent experiments treated with 6 different pools of EV. Viable cells stain green, dead cells red. (B) Evaluation of NFkB nuclear translocation in NRVM using the TLR4-specific inhibitor TAK242. DAPI mask was used to detect NFkB nuclear fraction. Dots in graphs present the numbers of different BMDM-derived EV tested in each experimental condition. (C) WB analysis and quantification of nuclear translocation of NFkB using the TLR4-specific inhibitor TAK242 (n= 4 independent experiments). Quantification data are presented as nuclear/cytosol ratio within the same treatment and expressed as mean fold change in fluorescence intensity versus w/o EV. All data are presented as mean ± SEM and analyzed by one-way ANOVAs with post-hoc multiple comparisons using Bonferroni correction (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). Mean, SEM and statistics are reported in full in Table S8.