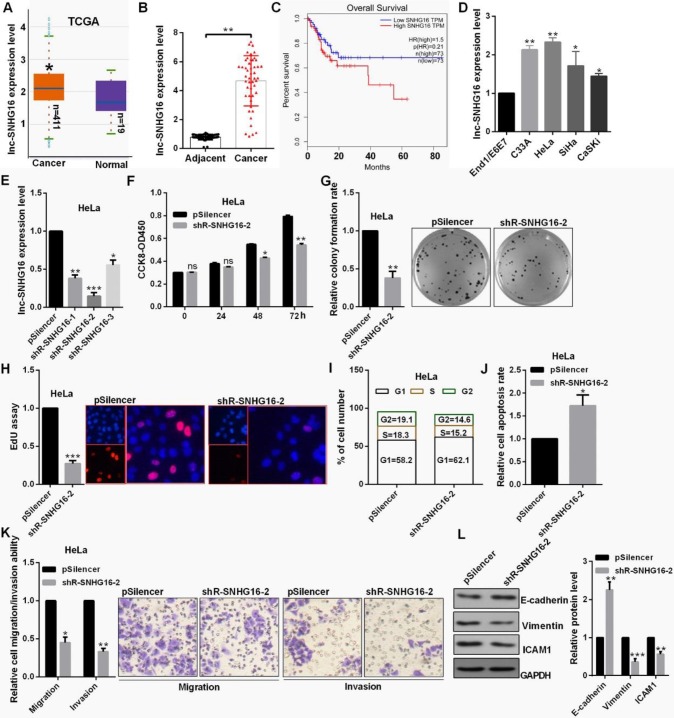
Figure 1.
lnc-SNHG16 functions an oncogene in cervical cancer. (A) TCGA database showed the level of lnc-SNHG16 in CC. (B) RT-qPCR showed the lnc-SNHG16 level in tumor and adjacent tissues. (C) Kaplan Meier plotter software showed the overall survival of CC patients with high or low expression of lnc-SNHG16. (D) RT-qPCR showed the level of lnc-SNHG16 in CC cells. (E) Efficiency of shRNAs for lnc-SNHG16 was identified by RT-qPCR. (F) Effect of shR-SNHG16-2 on cell viabilities was determined in HeLa by CCK8. (G) Relative colony formation rates of cells transfected with shR-SNHG16-2 in HeLa were detected. (H) EdU staining showed the proliferation ability of HeLa cells transfected with shR-SNHG16-2. (I) Flow cytometric analysis showed that shR-SNHG16-2 results in the cell cycle blocking in HeLa cell. (J) Flow cytometric assay revealed that shR-SNHG16-2 increased the apoptosis of HeLa cells. (K) Transwell assays revealed that shR-SNHG16-2 suppressed cell invasion and migration ability. (L) Western blot analysis of the indicated protein expression levels following transfection with shR-SNHG16-2 in HeLa cells. Experiments were performed 3 times, and data are presented as means ± SD.*P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001; ns, not significant.