Fig. 4.
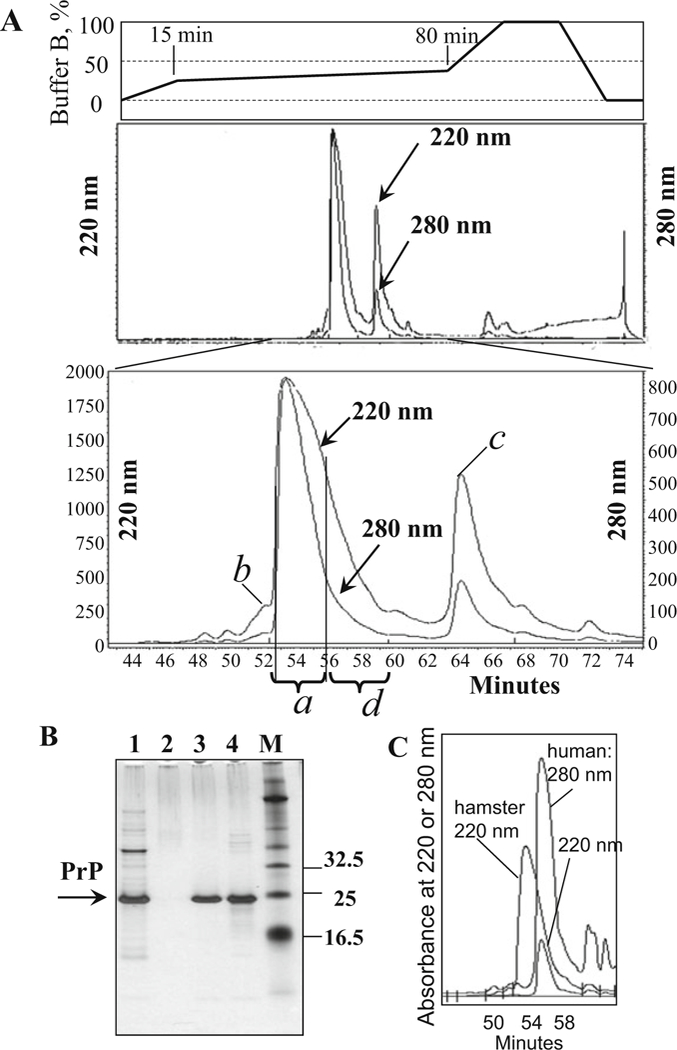
Purification of PrP on C4 column. (a) Typical HPLC profile of elution of mouse recombinant PrP. Major peak contains pure PrP (peak a); it is separated from the sub-peak containing PrP with oxidized methionines (peak b), from the peaks containing PrP with double glutathione adducts (peak c), and from other impurities. The right shoulder of the major HPLC peak (fractions d eluted at 56–60 min) is not collected; this shoulder may contain products of PrP degradation (see lane 4 in panel b). (b) Analysis of HPLC fractions in SDS-PAGE followed by silver staining: lane 1, PrP collected after IMAC and loaded onto C4 column; lane 2, HPLC flowthrough; lane 3, pure PrP collected from the major HPLC peak a; lane 4, right shoulder of the major peak (referred to as fraction d); and lane M, molecular marker. Lane 4 shows minor amounts of PrP degradation products that occur due to self-cleavage (seen as a smear with Mw < 23 kDa). The extent of PrP degradation may vary from preparation to preparation (see Note 3). (c) Comparative HPLC profile of elution of hamster and human recombinant PrP. The purification yield of human recombinant PrP (detection at 220 and 280 nm) is substantially lower than that of hamster PrP (detection at 220 nm)
