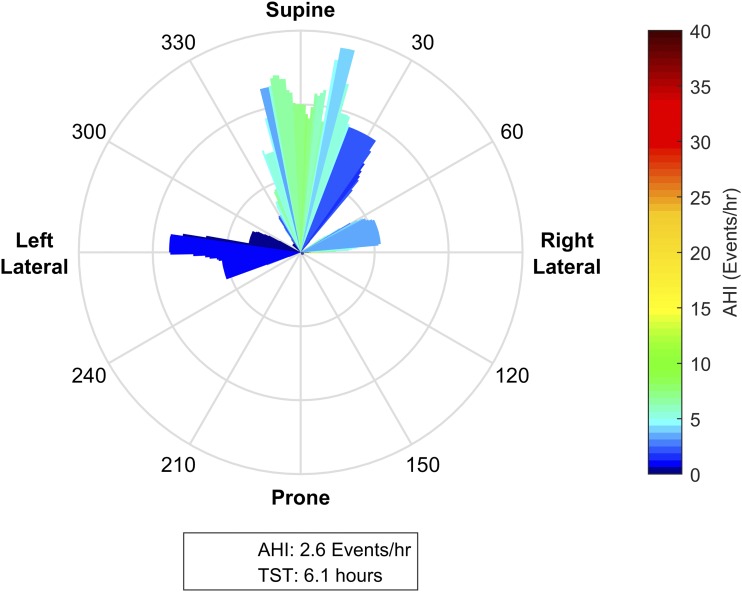
Figure 6. Subtle postural dependence.
This patient spent significant portions of the night within ± 30 degrees of supine, between 240–300 degrees (± 30 degrees of left lateral), and between 60–90 degrees (just supine of right lateral). While the patient has an overall apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) of 2.6 events/h, the posture-specific AHI is as high as 18 events/h when the patient is in the supine position. Notably, with torso rotation as little as 15 degrees to the left of supine, the position specific AHI reduces to approximately < 5 events/h. These data suggest that in this individual, effective treatment may be achieved with mild postural manipulations (ie, a small wedge under one shoulder). In patients who prefer to sleep supine, such interventions may be more tolerable than therapies that enforce lateral sleep.