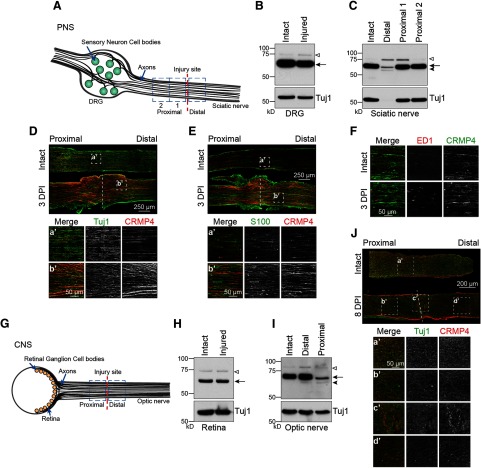
Figure 2.
The expression of CRMP4 is differentially regulated following CNS and PNS injury. A, Illustration of the sciatic nerve injury model used to examine the response to PNS injury. B, C, Immunoblot analysis of the CRMP4 expression pattern in DRG (B) and sciatic nerve (C) lysates from wild-type mice at 3 d following sciatic nerve transection. The nerve samples collected span 0–3 mm distal, 0–3 mm proximal (proximal 1), or 3–6 mm proximal (proximal 2) to the injury site. The data are representative of results obtained from seven mice. Open arrowhead, CRMP4L (75 kDa); arrow, CRMP4S (65 kDa); solid arrowhead, tCRMP4 (55 kDa). D–F, Representative images of longitudinal sections of intact and injured sciatic nerves to evaluate the colocalization of CRMP4 with Tuj1 (D), S100 (E), and ED1 (F), which are, respectively, markers of neurons, Schwann cells, and macrophages. G, Diagram of the optic nerve injury model used to examine the response to CNS axotomy. H, I, Immunoblot analysis of CRMP4 expression in retina (H) and optic nerve (I) lysates at 3 d following optic nerve transection. The nerve portions analyzed span from either 0–2 mm distal or 0–2 mm proximal to the injury site in the optic nerves. The data are representative of four independent replicates. Open arrowhead, CRMP4L (75 kDa); arrow, CRMP4S (65 kDa); solid arrowhead, tCRMP4 (55 kDa). J, Representative images of longitudinal sections of intact and injured optic nerves to evaluate the colocalization of CRMP4 a/b with the neuronal marker Tuj1.