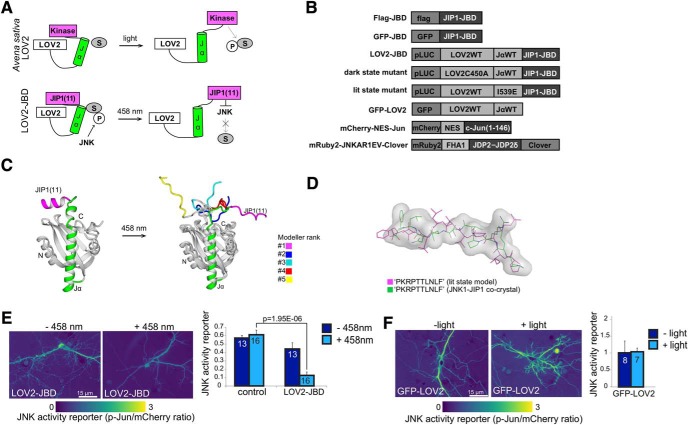
Figure 1.
Design and validation of the LOV2-JBD inhibitor. A, Schematic showing activation of LOV2 photo-domain from Avena sativa by light. The proposed mode of action of LOV2-JBD is shown in the lower panel where an 11-mer peptide inhibitor of JNK is released from the constrained conformation on photostimulation, facilitating binding to and inhibition of JNK. B, Constructs used in this study. C, Superimposed, top five lit-state model predictions for LOV2-JBD. In the top-ranked model, JIP1(11) (magenta) takes on a relaxed conformation projecting away from the core. D, JIP1(11) from the lit-state model (magenta) superimposed on the crystal structure of JIP1(11) from the JNK1-JIP1 co-crystal (green). E, mCherry-NES-Jun fluorescence provides a surrogate reporter of JNK activity in hippocampal neurons expressing mCherry-NES-Jun (control) or mCherry-NES-Jun with LOV2-JBD. Reporter activity is fluorescence intensity of phosphorylated c-Jun (P-Jun)/mCherry fluorescence intensity. Photostimulation of LOV2-JBD reduces JNK activity in hippocampal neurons; however (F) photostimulation of GFP-LOV2 does not. Data on dark-state and lit-state mutants are in Extended Data Figure 1-1. Mean data ± SEM and Student’s t test p values are shown. Cell numbers (from at least two experimental repeats) are indicated on the bars.