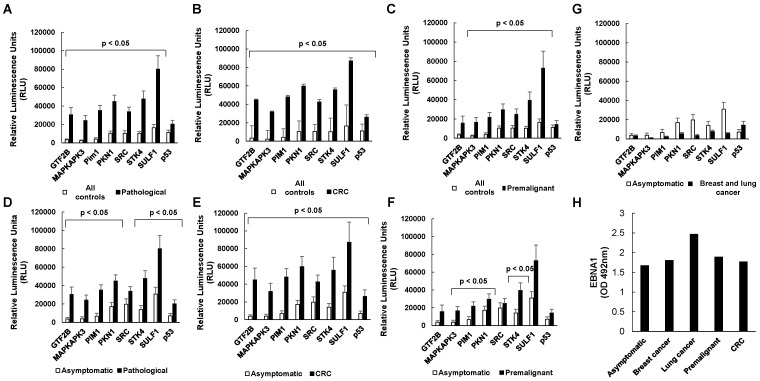
Figure 3.
Statistical analysis of autoantibody levels according to patients' groups. Autoantibodies against the eight targets could discriminate between the control and pathological group (A) and between controls and CRC patients (B). However, GTF2B and p53 could not discriminate between the control and premalignant subjects (C). All the autoantibodies but SRC could discriminate between the asymptomatic subjects and the pathological group (D). Moreover, the 8 autoantibodies could discriminate between the asymptomatic individuals and CRC patients (E). However, only MAPKAPK3, PIM1, PKN1, and STK4 could discriminate between asymptomatic and premalignant subjects (F). Furthermore, just p53 could differentiate between the asymptomatic individuals and breast and lung cancer patients (G). EBNA-I seroreactivity was analyzed as a test for the specificity of the assay, showing similar levels in all groups (H). Since >95% of the human population has been infected with the Epstein Barr virus, antibodies specific against EBNA1 would serve as specific control of the seroreactivity among all the analyzed groups. All controls: asymptomatic individuals, and breast and lung cancer patients.