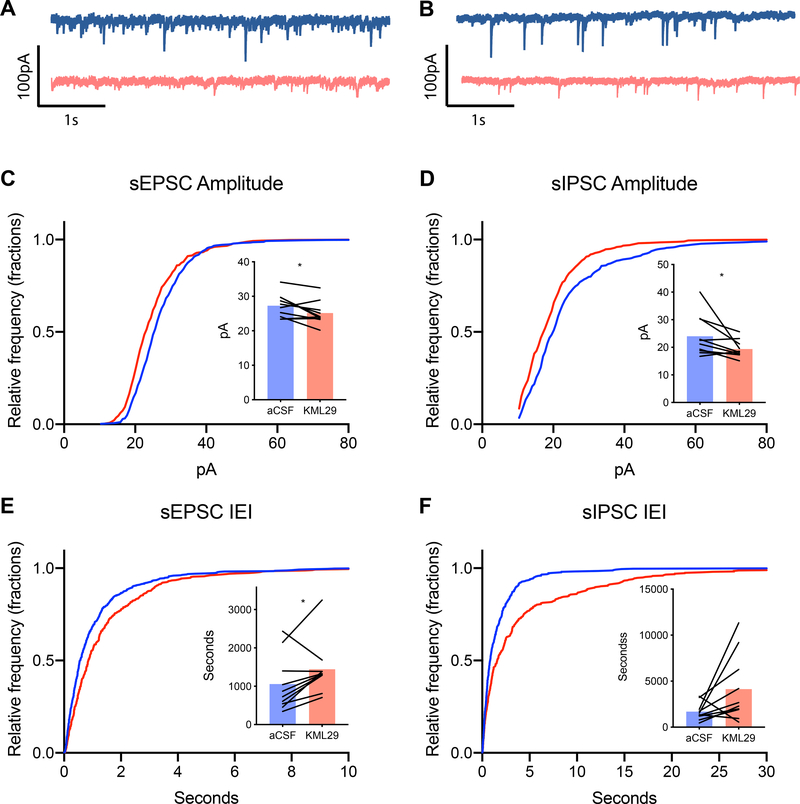
Figure 2.
Effect KML29 on spontaneous synaptic events. (A) Representative spontaneous excitatory post synaptic currents (sEPSC) traces and (B) spontaneous inhibitory post synaptic currents (sIPSC) during baseline (blue) and during application of 100nM KML29 (red). (C) Bath application of KML29 resulted in leftward shift in the cumulative distribution of sEPSC amplitude corresponding with reduced mean sEPSC amplitude (p<0.05) and (E) a rightward shift in sEPCS amplitude corresponding with an increased mean interevent interval of sEPSCs (p<0.05) compared to baseline. (D) The cumulative distribution of sIPSC amplitude was shifted leftward following application of KML29, which corresponding with decreased decreased mean sIPSC amplitude (p<0.05). (F) KML29 application right-shifted the cumulative distribution of sIPSC interevent interval, and increased mean sIPSC interevent interval (p>0.05). * denotes p<0.05.