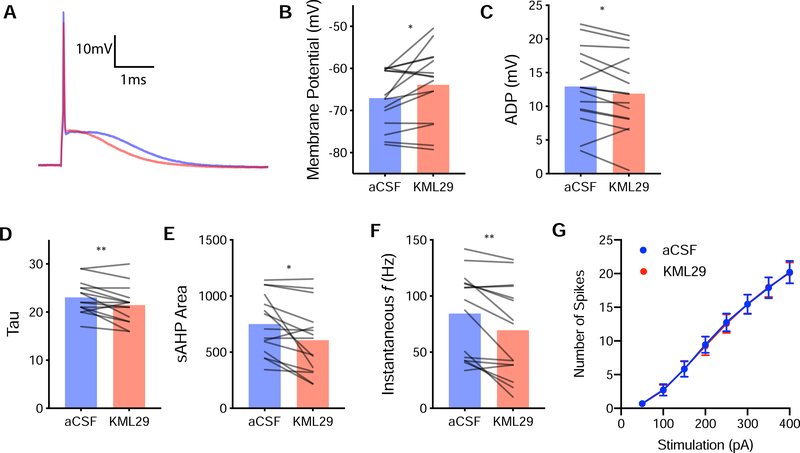
Figure 3.
Effects of KML29 on deep layer PL pyramidal neurons. (A) Representative action potentials during baseline (blue) or during application of 100nM KML29 (red) (B) Compared to baseline, KML29 increased resting membrane potential (p<0.05), (C) decreased after-deploraization (ADP, p<0.05), (D) decreased membrane time constant (Tau, p,0.01), (E) slow after-hyperpolarization (sAHP, p<0.05), (F) increases instantaneous frequency (p<0.01). (G) KML29 did not alter the relationship between the number of spikes and the stimulation strength. * and ** denotes p<0.05 and p<0.01 respectively.