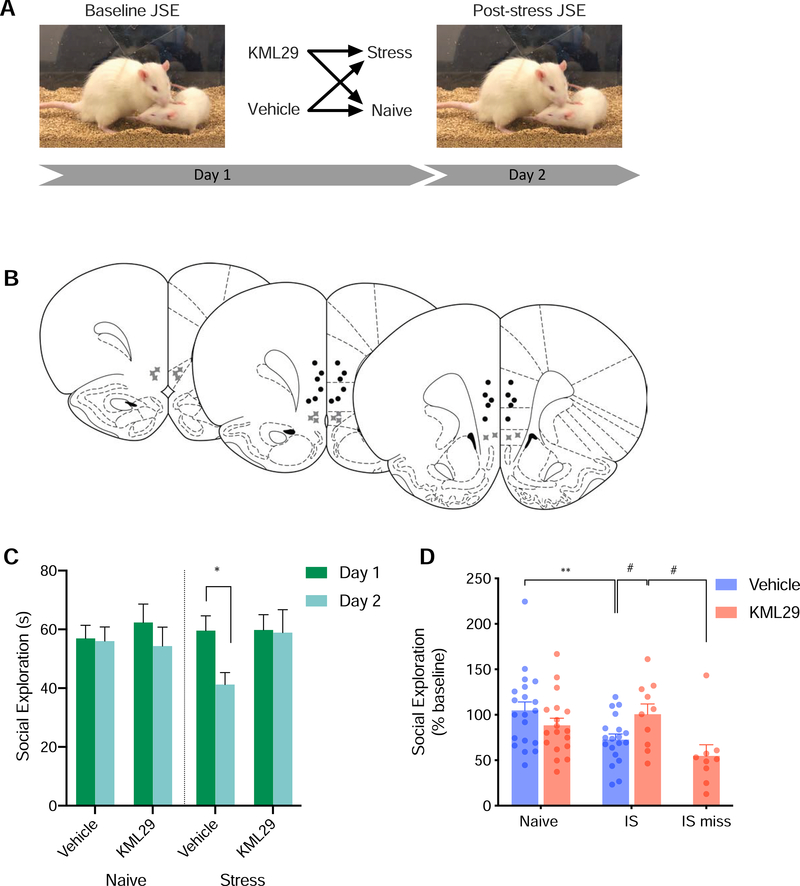
Figure 4.
(A) Diagram of behavioral procedure. (B) Schematic of cannula placements. Circles denote placements within the vmPFC while “X” symbols denote missed placements. (C) Mean (+SEM) social exploration. KML29 administered into the vmPFC during stress alters the behavioral consequences of the stressor. Stress decreased seconds engaged in social exploration in vehicle treated rats (p<0.01), but not KML29 treated rats (p=0.999). (D) Mean (+SEM with individual replicates) social exploration expressed as percent of baseline. Among rats that received vehicle injections, stress exposure (25 inescapable tail shocks) decreased social exploration compared with stress naïve rats (p<0.05). Rats in the miss condition received KML29 outside the vmPFC and showed less social exploration than rats that received KML29 in the vmPFC. * denotes p<0.05 with Sidak’s post hoc (C) Tukey’s post hoc (D). # denotes p<0.05 unprotected students t-test (D).