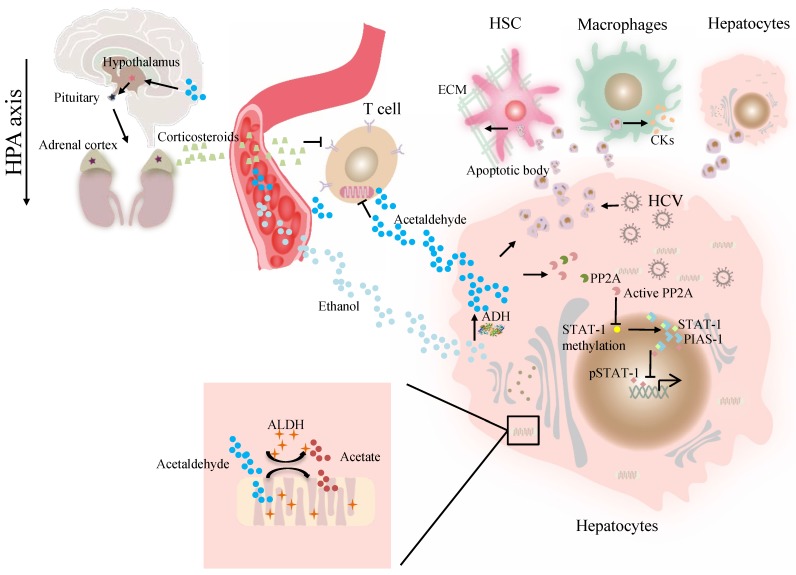
Figure 1.
The effect of ALDH in viral liver diseases. Ethanol is converted to acetaldehyde by the cytosolic enzyme ADH and the microsomal enzyme CYP2E1. Then acetaldehyde is converted to acetate by ALDH. Acetaldehyde directly suppresses cytokine production in T cells through the inhibition of aerobic glycolysis or stimulation of corticosterone release through HPA axis. Acetaldehyde also activates PP2A, leading to reduced STAT-1 methylation and formation of the PIAS-1-STAT-1 complex. Consequently, pSTAT-1 attachment to DNA is decreased, and ISG activation is inhibited. Acetaldehyde induces apoptosis in HCV -infected hepatocytes. Destruction of HCV-infected cells via AB release infectious HCV virions for de novo infection Kupffer cells, HSCs, and hepatocytes engulfed AB, potentially inducing of hepatic inflammation, fibrosis and apoptosis. Abbreviations: ALDH, aldehyde dehydrogenase; ADH, alcohol dehydrogenase; AB, apoptotic body; CYP2E1, cytochrome P-450 2E1; HPA, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal; ; HCV, hepatitis C virus; HSCs, hepatic stellate cells; ISG, interferon-stimulated genes; PP2A, protein phosphatase 2A; PIAS-1, protein inhibitor of activated STAT-1; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription.