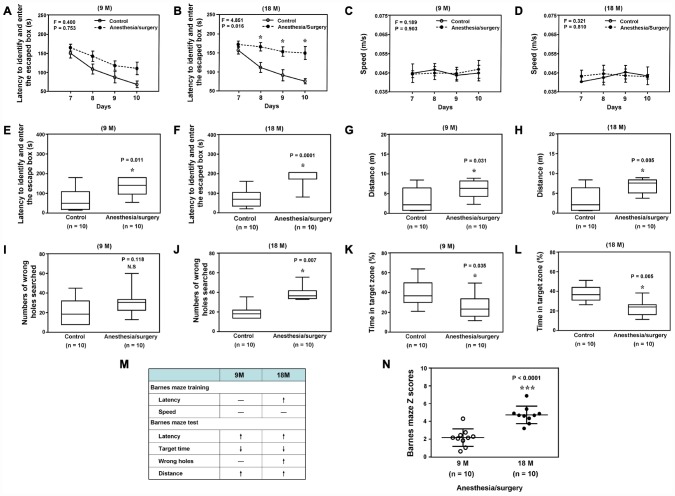
Figure 3.
Anesthesia/surgery induces age-dependent cognitive impairment in mice. Barnes maze training (latency to identify and enter the escape box) in the 9 (A) or 18 (B) months old mice. Barnes maze training (speed) in the 9 (C) or 18 (D) months old mice. Barnes maze testing (latency to identify and enter the escape box) in the 9 (E) or 18 (F) months old mice. Barnes maze testing (distance) in the 9 (G) or 18 (H) months old mice. Barnes maze testing (wrong holes) in the 9 (I) or 18 (J) months old mice. Barnes maze testing (time in target zone) in the 9 (K) or 18 (L) months old mice. The comparison of the qualitative (M) or quantitative (N) changes of the postoperative delirium-like behaviors between the 9 and 18 months old mice. The anesthesia/surgery causes a greater Barnes maze composite Z scores in the 18 months old mice than those in the 9 months old mice (N). N = 10 in each group. Two-way ANOVA with repeated measurement and post-hoc Bonferroni comparison was used to analyze the data in the (A–D). The Mann–Whitney U test was used to analyze the data presented in (E–L and N). * = P < 0.05.