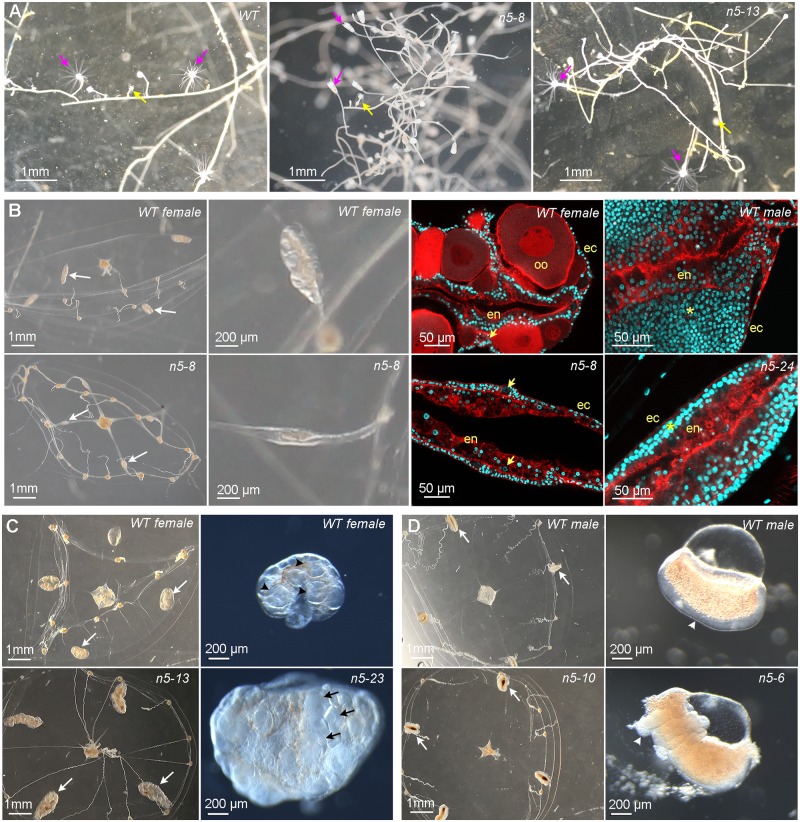
Fig 2. Phenotypes of Clytia MIHR mutants.
Light and confocal microscope images of MIHR mutant F0 polyp colonies and jellyfish. (A) Morphology of a wild-type (WT) colony, Z11, and two MIHR mutant colonies (n5-8 and n5-13), as indicated. All MIHR mutant colonies contained gastrozooid and gonozooid polyps (pink and yellow arrows, respectively); however, the connecting stolons in some mutant colonies (see Table 1) were convoluted and frequently detached from the glass substrate, while stolons of WT colonies and the other mutant colonies were straight and adhered tightly. (B) Phenotypes of fully grown WT (top row) and mutant n5-8 or n5-24 (bottom row) jellyfish. Mutant and WT jellyfish show very similar morphology, but gonads developed poorly in these mutants, as shown by white arrows in the first column and at higher magnification in the second column. The third and fourth columns are confocal microscope images through the gonads of adult jellyfish from females and males, respectively; nuclei are stained with Hoechst 33342 (cyan) and F-actin with Phalloidin (red). In the n5-8 female gonad, small oocytes (arrows) can be detected between the endodermal (en) and ectodermal (ec) layers, but no large growing oocytes (oo) are present compared to the WT female gonad. In the n5-24 male gonad, the spermatogenic zone (asterisk) between endoderm and ectoderm is much thinner than in the WT male gonad. (C) Comparison of mutant n5-23 and n5-13 (bottom row) female medusae gonads (white arrows) swollen by an accumulation of large oocytes to WT (Z11) female medusae (top row). Right panels show gonads dissected from 3-week-old n5-23 medusae 10 hours after a light cue that induced spawning in the WT but not the mutant gonad. Black arrowheads indicate large growing oocytes in the WT gonad and black arrows indicate fully grown oocytes in the mutant gonad. (D) Adult mutant n5-10 and n5-6 male medusa (bottom row) compared to WT (Z13) male medusae (top row) have deformed gonads (white arrows). Right panels show isolated gonads, illustrating the thickened and irregular spermatogenic layer (arrowheads) in the mutant. Scale bars as indicated. MIHR, MIH receptor.