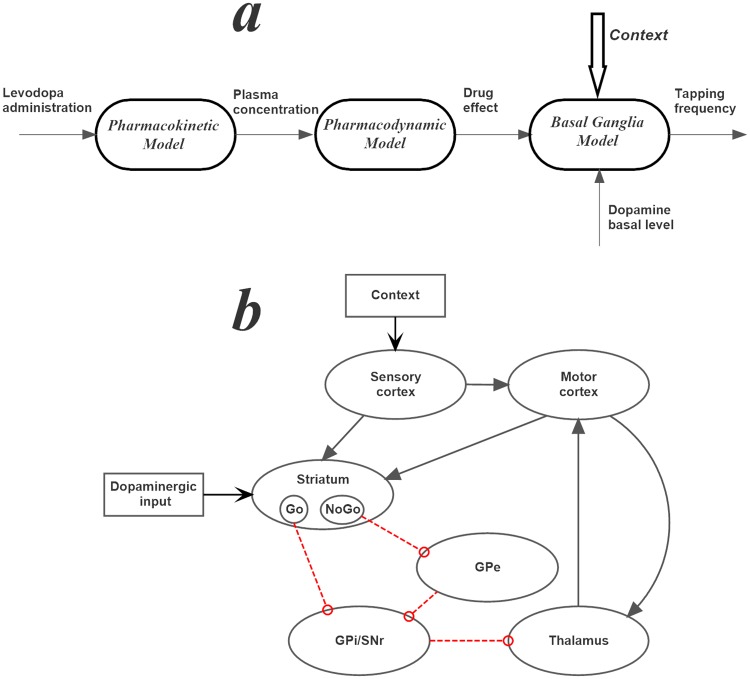
Fig 1.
a) General structure of the mathematical model used in this work. The first part (pharmacokinetics) is described via a two-compartmental model of LD concentration in plasma. The second (pharmacodynamics) describes the concentration of the drug in the brain and its effect on striatal neurons. The third (neurocomputational model) describes action selection by the basal ganglia during a finger tapping test, as a function of the dopaminergic input. b) Topological organization of the neurocomputational model, where black lines with arrows denote excitatory connections, and red lines with open circles inhibitory connections. GPe: Globus Pallidus pars externa; GPi/SNr: Globus Pallidus pars interna/Substantia Nigra pars reticulata.