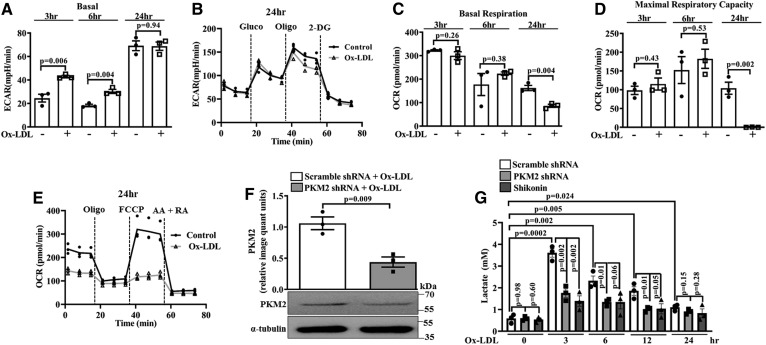
Fig. 2.
Ox-LDL induces aerobic glycolysis in BMDMs. Extracellular flux analysis and lactate measurement. A: Basal ECAR in control and Ox-LDL-treated (40 μg/ml) BMDMs (n = 3). B: Real-time changes in ECAR in control and Ox-LDL-stimulated (40 μg/ml) BMDMs (n = 3). C: Basal OCR in control and Ox-LDL-treated (40 μg/ml) BMDMs (n = 3). D: Maximal respiratory capacity in control and Ox-LDL-treated (40 μg/ml) BMDMs (n = 3). E: Real-time changes in OCR after pretreatment with Ox-LDL (40 μg/ml) (n = 3). F: Western blot analysis of PKM2 expression in Ox-LDL-activated (40 μg/ml) BMDMs after knockdown with PKM2 shRNA (1.5 × 106 PFU, 48 h) (n = 3). G: Time-dependent response of Ox-LDL (40 μg/ml) on extracellular l-lactate release in Shikonin- or PKM2 shRNA-pretreated BMDMs (n = 3). Values represent mean ± SEM.