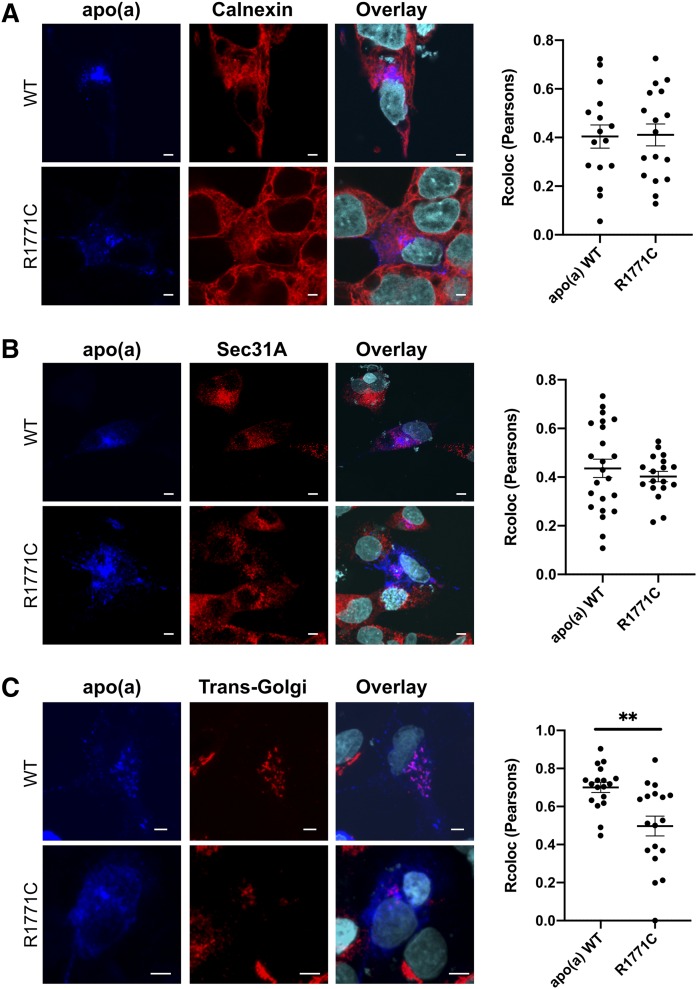
Fig. 5.
The R1771C apo(a) shows a reduced progression through the secretory pathway. HepG2 cells were transfected with 500 ng of either WT or R1771C apo(a)-GFP cDNA and fixed and imaged by confocal microscopy at 24 h. Cells were permeabilized and stained with antibodies for apo(a), the ER protein, calnexin, the CopII protein, Sec31A, and the Golgi marker protein, TGOLN2. The apo(a) antibody was detected with an anti-mouse Alexa Fluor® 647 secondary antibody (blue), the calnexin, the Sec31A and TGOLN2 antibodies were detected with an anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor® 555 secondary antibody (red). Multiple fields of view were visualized and representative images are shown. Images are also shown as overlays with a DAPI nuclear stain (cyan). Colocalization of the Alexa Fluor® 647 signal detecting apo(a) with the Alexa Fluor® 555 signal detecting the various compartment markers was assessed in confocal images of transfected cells by calculating the Pearson’s correlation coefficient using the Colocalization Finder plugin of ImageJ. Data represents mean ± SEM for at least fifteen individual cells. **P < 0.01 for R1771C versus WT apo(a).