Figure 3.
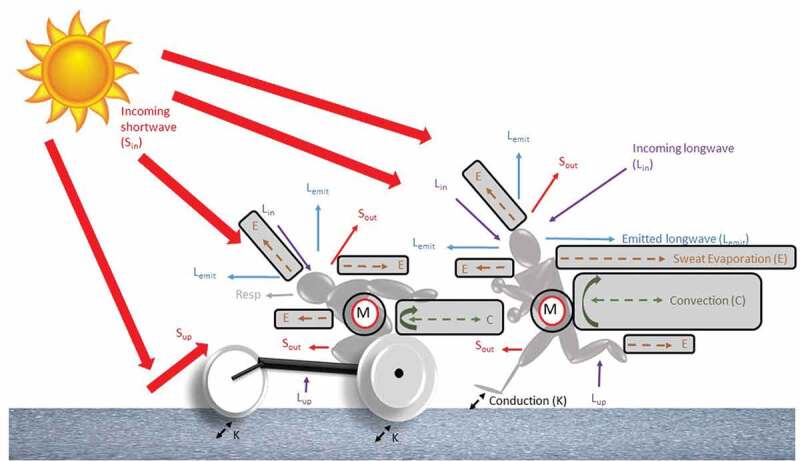
Heat exchange between the environment and the human body in an outdoor environment. In normal conditions, heat balance will increase due to an increase in metabolic heat production (M) and radiation in both shortwave (Sin and Sup) and longwave (Lin and Lup) radiation. A human usually loses heat through convection (C), evaporation (E), respiration (resp) and emitted longwave radiation (Lemit). The grey boxes highlight the heat exchange pathways (convective and evaporative heat loss and metabolic heat production) affected as a result of the Paralympic athlete’s disability, discussed in the review.
