Figure 2.
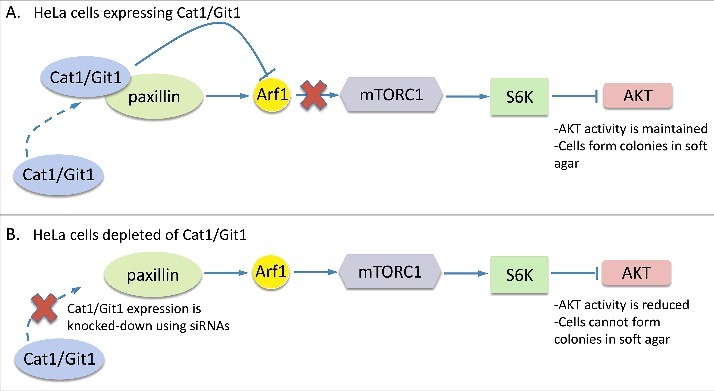
Diagram showing the mechanism through which Cat1/Git1 promotes HeLa cervical carcinoma cell transformation. A) When expressed in HeLa cells, Cat1/Git1 associates with paxillin to prevent it from functioning as a negative regulator of cellular transformation. Specifically, the interaction between Cat1/Git1 and paxillin inhibits the ability of paxillin to activate the Arf1-mTORC1-P70S6 kinase (S6K) pathway, which ensures that the necessary level of AKT activation required for supporting soft agar colony formation is met. B) However, under conditions where Cat1/Git1 expression is knocked-down in HeLa cells using siRNAs, paxillin is now able to stimulate the activation of the Arf1-mTORC1-P70S6 kinase pathway and inhibit AKT activation. These cells are no longer capable of forming colonies in soft agar.
