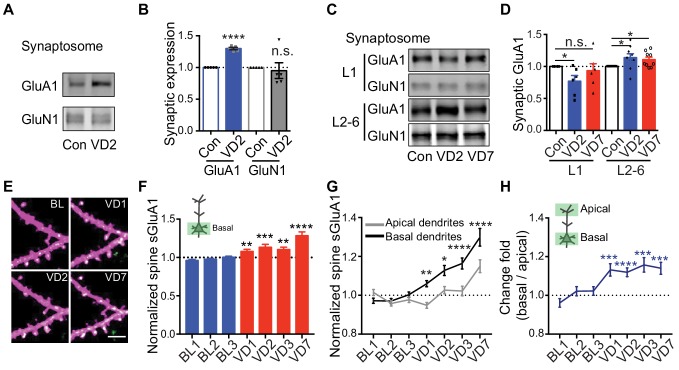
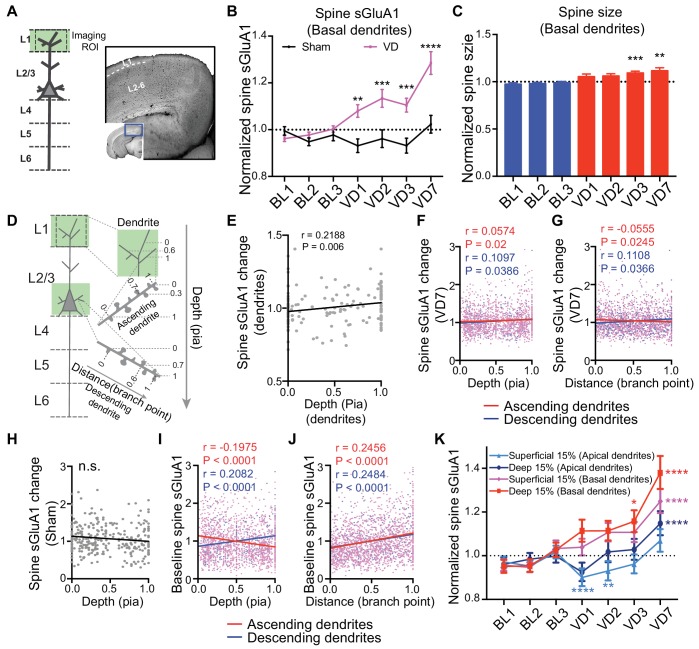
Figure 5. Depth-dependent changes in spine sGluA1 expression after visual deprivation.
(A and B) Synaptic GluA1 and GluN1 levels in V1 from 2 days’ enucleated or sham-surgery mice (n = 5; Student’s t-test). (C and D) Synaptic GluA1 levels from superficial (L1) and deep (L2-6) layers of V1 (n = 6–9; Student’s t-test). (E and F) Changes in spine sGluA1 on basal dendrites of V1 L2/3 neurons following VD (n = 40 dendrites from six mice; one-way ANOVA). Scale bar: 5 μm. (G) Changes in spine sGluA1 on basal and apical dendrites from the same neurons following VD (n = 16 neurons from seven mice; repeated measure two-way ANOVA). (H) Change ratios of basal dendrites to apical dendrites of the same neurons following VD were significantly larger than 1 (n = 16 neurons from seven mice. one sample t-test). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. n.s., not significant; *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001.