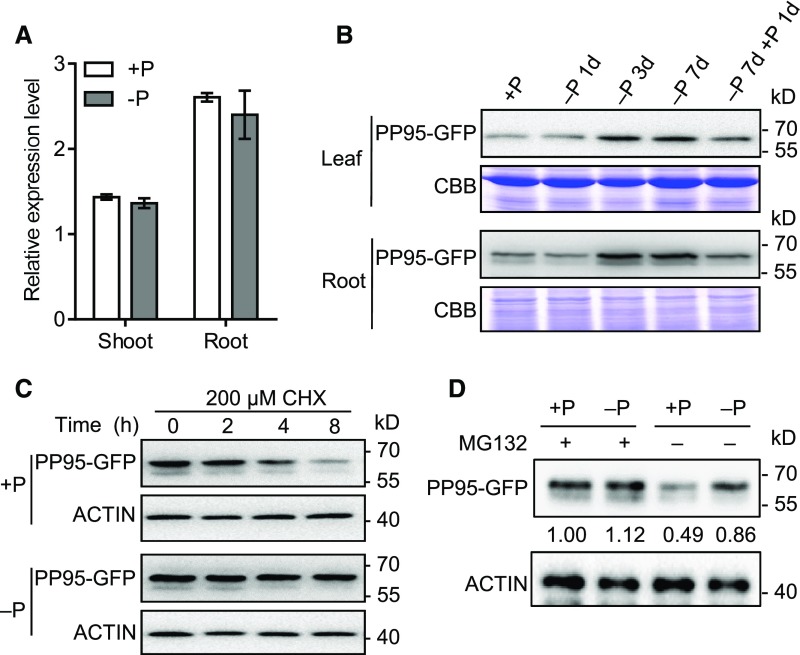
Figure 8.
PP95 Is More Stable under Pi-Deficient Versus Pi-Sufficient Conditions.
(A) Relative PP95 expression levels in the shoots and roots of plants grown in solution with (+P; 200 μM) or without (–P; 0 μM) Pi.
(B) PP95 protein levels in plants under different durations of Pi starvation. Proteins were extracted from ProPP95:gPP95-GFP/PP95-10 transgenic plants grown under +P conditions for 10 d and transferred to –P conditions for 1 to 7 d, followed by Pi resupply for 1 d. PP95-GFP proteins were detected by immunoblotting after SDS-PAGE using an anti-GFP antibody. Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) staining was used as a loading control.
(C) Effect of CHX treatment on PP95 in rice. Fourteen-day-old ProPP95:gPP95-GFP/PP95-10 transgenic plants grown under +P and –P conditions were treated with the protein synthesis inhibitor CHX for the indicated durations. PP95-GFP extracted from roots was detected by immunoblotting using an anti-GFP antibody. ACTIN detected using anti-ACTIN antibody was used as a control.
(D) Effect of MG132 treatment on PP95 degradation in rice. ProPP95:gPP95-GFP/pp95-10 transgenic plants grown under +P and –P conditions were treated with or without MG132 for 24 h. PP95-GFP extracted from roots was detected by immunoblotting using an anti-GFP antibody. ACTIN was used as a control. Values represent relative quantification of PP95-GFP proteins in related samples.