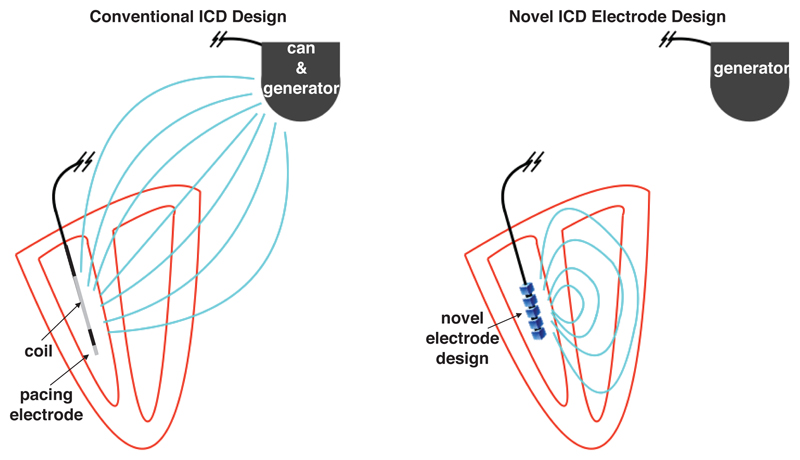
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of conventional ICD electrode configuration (left) and proposed novel ICD electrode configuration (right). In the conventional ICD during a defibrillation shock, the RV coil is used to generate an electric field with shock vector between the coil and the can as the ground (field shown as light blue lines), thus generating significant extra-cardiac field and a lack of directionality. The tip of the RV coil acts as a pacing electrode when delivering ATP. In the proposed novel configuration, the RV electrode generates a field which is confined within the heart and is steerable, not requiring the generator to act as a ground.