FIG 1.
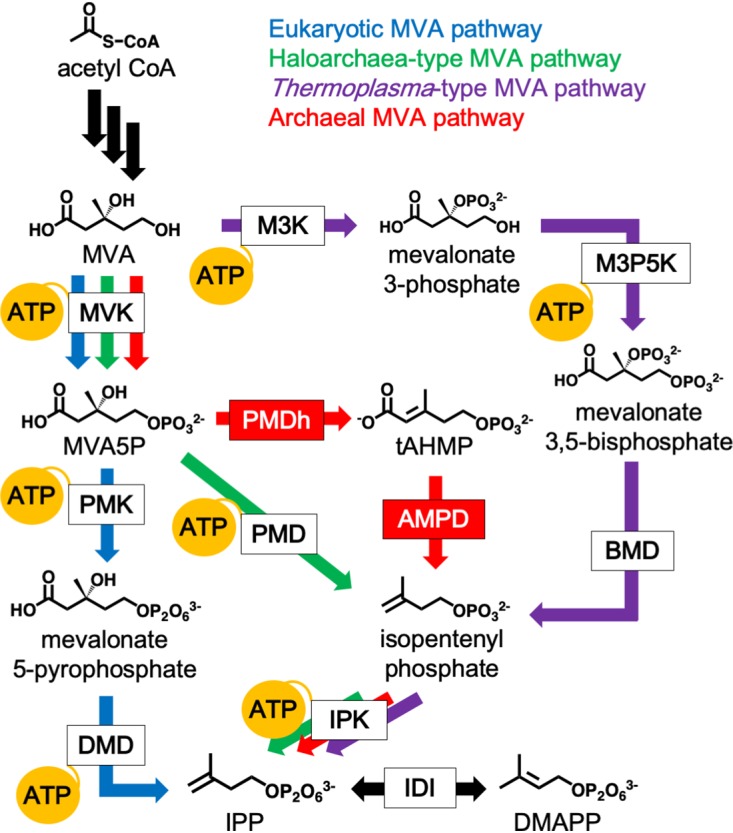
The variety of MVA pathways and their ATP consumption. The canonical eukaryotic MVA pathway, which is utilized by almost all eukaryotes, some bacteria, and archaea of the order Sulfolobales, is shown by blue arrows. The haloarchaea-type MVA pathway, found in all archaea of the class Halobacteria and in some bacteria of the phylum Chloroflexi, is shown by green arrows. The Thermoplasma-type MVA pathway, utilized in archaea of the order Thermoplasmatales, is shown by purple arrows. The archaeal MVA pathway, probably conserved in a wide range of archaea, is shown by red arrows. Black arrows indicate common reactions. The reactions that consume ATP are indicated by yellow balloons. The abbreviated names of enzymes are boxed, and those in red boxes, i.e., PMDh and AMPD, were discovered in a recent study (6). BMD, bisphosphomevalonate decarboxylase; DMD, diphosphomevalonate decarboxylase; M3K, mevalonate 3-kinase; M3P5K, mevalonate 3-phosphate 5-kinase; PMD, phosphomevalonate decarboxylase; PMK, phosphomevalonate kinase.
